In The United States Today Can Be Fun For Everyone
2017 premium boosts emerged: A private non-profit web service by Charles Gaba posts a comprehensive.
tracker of rate filings consisting of forecasted in general, weighted average rate changes for the specific market. Kaiser Family Foundation has an assessment of 2017 premium changes and company participation. It exists with the following declaration," in general, 23 percent seems to be the number to take a look at for requested increases overall. "During September and October it was up to state regulators to either approve or change those requests." Marketplace Premiums after Shopping, Changing, and Premium Tax Credits, 2015-2016. Rates then go through review prior to being completed in the fall, prior to the yearly Health Insurance coverage Market Open Registration Period (how does electronic health records improve patient care). Neither the proposed nor final rates offered by any private provider supply a trusted basis for anticipating what common Market consumers will pay in the following year. Consumers 'actual health insurance coverage premiums. Annual premiums for employer-sponsored family health protection reached $ 18,142 this year, up 3 percent from last year, with workers on typical paying$ 5,277 towards the expense of their coverage. Summary Complete Report.
Kaiser/HRET survey, released 9/2016. 2015 Company Health Benefits Survey - what is home health care. Annual premiums for employer-sponsored family health protection include a modest boost( 4 percent) in the typical premiums for both single and family coverage in the past year. Complete Report 2014 Company Health Advantages Survey. Yearly premiums for employer-sponsored household health protection reached$ 16,834 that year, up 3 percent from the previous year, with employees on typical paying$ 4,823 towards the cost of their coverage. Summary of Findings.

Complete report. Motorists of Health Insurance Premium Modifications for 2017- An issue brief produced by the American Academy of Actuaries' Person and Small Group Markets Committee, "Motorists of 2017 Medical Insurance Premium Modifications." There are both upward and downward pressures on premiums for 2017, however" for the individual and small group markets as an entire, the factors driving premium boosts control," said Academy Senior Health Fellow Cori Uccello. The 1 year moratorium of the medical insurance service provider charge will partly balance out these increases. "Motorists of 2016 Health Insurance Coverage Premium Modifications. The Affordable Care Act (ACA )developed three premium stabilization programs: the irreversible risk adjustment program and the transitional danger corridor and reinsurance programs.
They have actually provided some stability for the very first three years of the implementation of the Affordable Care Act's individual and little group market reforms; the reinsurance program is credited with lowering market premiums for 2014 by 10 to 14 percent and for 2015 by 6 to 11 percent. Download report- trend-survey-2016. pdf 2015 Segal Health Plan Cost Trend Survey-( compare to 2016, above) Download report- 2015trendsurvey.pdf Analysis of 2016 Premium Changes and Insurer Participation in the ACA's Health Insurance Marketplaces- report by Kaiser Household Foundation, June 24, 2015 [ Excerpt]. Every year, open enrollment for health insurance coverage prepares takesplace from November to December. If you don't have a certifying life occasion throughout the year, then this is the time to look around to ensure you're paying the best cost for the best coverage. If you're wondering just how much is medical insurance, here's how the rates have actually altered over the previous few years, plus ways you can decrease your month-to-month premium. And according to the Kaiser Household Structure, open enrollment for 2019 saw a typical month-to-month Drug Abuse Treatment premium of$ 612 for Health care Market prepares that were readily available in 39 states. Compared to prior years, that's just 1.4% less than 2018($ 621), but about 29% more than 2017( $476 ). Open registration for 2019 took place between Nov. 15, 2018. While$ 612 was the national average, it is essential to consider how regular monthly premiums alter from state to state. While 39 states use the federal Healthcare Market, 12 states run their own marketplaces, and information is not always reported for every state. Market Average Premiums and Typical Advanced Premium Tax Credit( APTC) Location Average Premium Average Premium After APTC United States$ 612$ 143 Alabama$ 669$ 123 Alaska$ 746$ 174 Arizona$ 596$ 195 Arkansa$ 513$ 173 California$ 582 $168 Colorado$ 710$.
240 Connecticut $625 $264 Delaware$ 842 $202 District of Columbia$ 469 $447 Florida$ 605$ 100 Georgia$ 598$ 127 Hawaii$ 664 $214 Idaho N/A N/A Illinois$ 646 $207 Indiana $491$ 259 Iowa$ 918$ 126 Kansas $661$ 149 Kentucky $595 $196 Louisiana $613 $182 Maine$ 675$ 155 Maryland $552 $191 Massachusetts$ 392$ 204 Michigan $498$ 171 Minnesota$ 455$ 279 Mississippi $641 $76 Missouri$ 645$ 158 Montana$ 670 $174 Nebraska$ 866 $80 Nevada$ 509 $152 New Hampshire $540 $237 New Jersey $511 $235 New Mexico $483 $174 New york city $618 $224 North Carolina $729 $114 North Dakota $502 $165 Ohio $538 $234 Oklahoma $674 $77 Oregon $560 $222 Pennsylvania $654 $193 Rhode Island $443 $174 South Carolina $669 $116 South Dakota $652 $137 Tennessee $659 $141 Texas $544 $118 Utah $459 $82 Vermont $573 $148 Virginia $687 $175 Washington $551 $286 West Virginia $937 $265 Wisconsin $700 $161 Wyoming $960 $125 Employer-sponsored health insurance strategy expenses are trending upwards. The expense of family protection has actually increased 22% considering that 2014. When it pertains to the expense of employer-sponsored health insurance, you require to think about that your company might contribute to the expense of your plan as part of your employee advantages. While the average expense of a family strategy is $20,576, the data reveals that workers are just paying about $6,015 annually, and the employer is paying the rest. You should also make in between 100% and 400% of the Federal Hardship Line( FPL), or receive Medicare, Medicaid, Kid's Health.

Unknown Facts About How Much Does Medicare Pay For Home Health Care Per http://cashzwtg729.cavandoragh.org/indicators-on-access-and-quality-of-health-services-quizlet-you-need-to-know Hour
Insurance Coverage Program, or other types of public assistance. In the 48 contiguous United States( omitting Alaska and Hawaii )the FPL is$ 48,560 for a private or$ 100,400 for a household of 4. If you do not certify for an aid, the percentage of your income you need to cover your health insurance coverage expenses increases dramatically. Medical insurance rates also increase by age. The Kaiser Household Foundation found that in 21 %of U.S. counties, people with a$ 50,000 income would pay a different percentage for medical insurance because of their age: If they were 27, they would pay about 7% of their income for the lowest-cost plan nationallyIf they were 40, they would need to pay more than 10 %of their earnings If they were 60, they would pay 17% of their.
income for the same plan Now that you comprehend the typical expenses of health insurance coverage and how to receive an aid, the concern you may have is: What is going to make the rate of your health insurance coverage go up or down? Factors that will affect your expense Substance Abuse Center of health insurance coverage might include: If you certify for an aid or notYour ageWhere you liveHow many individuals are covered by the strategy (specific vs.
Facts About What Services Does Home Health Care Provide Revealed
But cases are accelerating in the U.S., which has actually become the global center for the virus, with roughly 6 million validated cases and 183,000 deaths or the equivalent of one in 5 COVID-19 deaths worldwide. "It's truly discouraging to have to divert so much political energy towards what must be a no-brainer." One strength of the Canadian system to shine https://telegra.ph/what-does-what-is-the-impact-of-managed-care-on-cost-do-10-21 through during the pandemic is that everybody is guaranteed, Martin said.
Healthcare facilities work with a single insurance provider, she said, and that implies care is better collaborated throughout organizations. "Anyone that needs COVID care is going to get it," she said. Dr. Ashish Jha, who has actually directed the Harvard Global Health Institute and now functions as the dean of the Brown University School of Public Health, has a slightly various take.
and Canada present "a reflection that has nothing to do with the underlying health system" however rather reflects leaders and their political will and concerns. While America's health care system is amongst the world's finest in terms of innovation and technology, Addiction Treatment Facility Jha said that U.S. politicians have actually shown themselves to be reluctant to trade off short-term pain of lockdowns and task losses for a long-lasting public health crisis and financial instability.
They also didn't ramp up screening rapidly enough to efficiently keep track of when and where outbreaks would occur and repeatedly undermined the public health neighborhood in its efforts to effectively react to the virus. He stated leaders in the U.S. have actually not offered a clear consistent message or definitive management to join the country and get everyone relocating the very same direction.

" It's actually discouraging to need to divert a lot political energy towards what must be a no-brainer," Jha stated. "This is the time when everybody who requires to be tested, is evaluated everyone who requires to be looked after is looked after." Which starts with consistent access to effective healthcare, he stated.
The 20-Second Trick For How Much Would Single Payer Health Care Cost Per Person
gone into lockdown under coronavirus, Sen. Bernie Sanders revealed on April 8 that he had pulled the plug on his presidential run. A week later he endorsed previous Vice President Joe Biden. After contests in 28 states and two territories, his course to winning the Democratic nomination had narrowed substantially in spite of an early edge.
His project has proposed offering "every American a brand-new choice, a public health choice like Medicare" to make insurance coverage more inexpensive. As Potter sees COVID-19 rage in the U.S., the previous health care communications executive said Americans live in "worry of having huge out-of-pocket costs without guarantee that we'll have our expenditures covered." With the variety of uninsured Americans nearly double what they were before novel coronavirus, according to some quotes, Potter said that is not sustainable.
reaction to the coronavirus pandemic was below par, if not the worst, on the planet. This pandemic might bring the nation to a snapping point, Potter stated, pressing more Americans to require a health care system that exceeds the reforms of the Affordable Care Act, which the Trump administration has actually repeatedly attacked and tried to take apart.
" You will see this campaign resurface to attempt to scare people far from change," he said. "It takes place whenever there is a considerable push to change the health care system. The industry wants to secure the status quo." There's no ideal healthcare system, and the Canadian system is not without defects, Flood said.
In June 2019, New Democrat Celebration Leader Jagmeet Singh proposed expanding Canada's pharmaceutical drug coverage. The ultimate goal of these modifications that have actually been discussed in varying degrees for several years is to incorporate oral, vision, hearing, psychological health and long-lasting care to develop "a head to toe Visit this website healthcare system." And yet it is natural for Canadians to compare systems with their neighbors and simply "feel grateful for what they have (why is health care so expensive)." She says that sort of complacency has actually insulated Canada's system from additional improvements that produce typically much better outcomes for lower costs, as in the United Kingdom, the Netherlands or Switzerland.
How Much Does Medicare Pay For Home Health Care Per Hour for Dummies
Healthcare reform has been an ongoing dispute in the U.S. for decades. 2 terms that are frequently used in the discussion are universal health care coverage and a single-payer system. They're not the very same thing, despite the truth that people in some cases utilize them interchangeably. how does electronic health records improve patient care. While single-payer systems normally include universal protection, numerous nations have accomplished universal coverage without utilizing a single-payer system.

Universal protection describes a healthcare system where every individual has health coverage. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, there were 28.1 million Americans without medical insurance in 2016, a sharp decrease from the 46.6 million who had been uninsured prior to the application of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
Thus, Canada has universal health care coverage, while the United States does not. It is necessary to keep in mind, nevertheless, that the 28.5 million uninsured in the U.S. consists of a substantial variety of undocumented immigrants. Canada's government-run system does not offer coverage to undocumented immigrants. On the other hand, asingle-payer system is one in which there is one entityusually the federal government accountable for paying healthcare claims.
So although it's a form of government-funded health protection, the funding originates from 2 sources rather than one. People who are covered under employer-sponsored health insurance or individual market health plans in the U.S. (including ACA-compliant plans) are not part of a single-payer system, and their health insurance is not government-run.
There are presently a minimum of 16 nations that provide some type of a single-payer system, consisting of Canada, Norway, Japan, Spain, the UK, Portugal, Sweden, Brunei, and Iceland. Most of the times, universal protection and a single-payer system go together, since a nation's federal government is the most likely candidate to administer and spend for a health care system covering countless people.
The smart Trick of What Is Health Care Flexible Spending Account That Nobody is Discussing
However, it is very possible to have universal protection without having a complete single-payer system, and many nations around the world have done so. Some nations operate a in which the federal government supplies standard healthcare with secondary coverage offered for those can afford a higher requirement of care. Denmark, France, Australia, Ireland, Hong Kong, Singapore, and Israel each have two-tier systems.
Mingled medication is another phrase that is frequently mentioned in conversations about universal coverage, however this design really takes the single-payer system one action even more - what might happen if the federal government makes cuts to health care spending?. In a socialized medication system, the federal government not only spends for healthcare however operates the medical facilities and employs the medical staff. In the United States, the Veterans Administration (VA) is an example of interacted socially medicine.
However in Canada, which also has a single-payer system with universal coverage, the healthcare facilities are privately operated and medical professionals are not used by the federal government. they simply bill the government for the services they provide. The primary barrier to any socialized medicine system is the government's ability to successfully fund, handle, and update its standards, equipment, and practices to offer optimum healthcare.
Not known Factual Statements About Which Of The Following Is The Largest Single Source Of Reimbursement For Home Health Care Services?
2017 premium increases emerged: A personal non-profit web service by Charles Gaba posts a detailed.
Kaiser/HRET survey, released 9/2016. 2015 Employer Health Benefits Survey - how much do home health care agencies charge. Annual premiums for employer-sponsored household health coverage consist of a modest increase( 4 percent) in the typical premiums for both single and family protection in the past year. Full Report 2014 Company Health Benefits Study. Annual premiums for employer-sponsored household health coverage reached$ 16,834 that year, up 3 percent from the previous year, with employees usually paying$ 4,823 towards the cost of their coverage. Summary of Findings.

Full report. Chauffeurs of Health Insurance Premium Changes for 2017- An issue short produced by the American Academy of Actuaries' Individual and Small Group Markets Committee, "Drivers of 2017 Medical Insurance Premium Modifications." There are both upward and down pressures on premiums for 2017, but" for the private and small group markets as a whole, the factors driving premium increases dominate," said Academy Elder Health Fellow Cori Uccello. The one-year moratorium of the health insurance company fee will partially offset these boosts. "Motorists of 2016 Medical Insurance Premium Changes. The Affordable Care Act (ACA )developed three premium stabilization programs: the long-term danger change program and the transitional danger passage and reinsurance programs.
They have actually provided some stability for the first 3 years of the execution of the Affordable Care Act's specific and little group market reforms; the http://cashzwtg729.cavandoragh.org/indicators-on-access-and-quality-of-health-services-quizlet-you-need-to-know reinsurance program is credited with decreasing market premiums for 2014 by 10 to 14 percent and for 2015 by 6 to 11 percent. Download report- trend-survey-2016. pdf 2015 Segal Health Insurance Expense Pattern Study-( compare to 2016, above) Download report- 2015trendsurvey.pdf Analysis of 2016 Premium Modifications and Insurance Company Involvement in the ACA's Medical insurance Marketplaces- report by Kaiser Household Foundation, June 24, 2015 [ Excerpt]. Every year, open registration for medical insurance prepares takeslocation from November to December. If you do not have a qualifying life event throughout the year, then this is the time to look around to ensure you're paying the finest rate for the ideal coverage. If you're wondering just how much is medical insurance, here's how the rates have actually changed over the previous few years, plus ways you can lower your monthly premium. And according to the Kaiser Household Foundation, open enrollment for 2019 saw a typical regular monthly premium of$ 612 for Healthcare Market plans that were offered in 39 states. Compared to prior years, that's just 1.4% less than 2018($ 621), but about 29% more than 2017( $476 ). Open enrollment for 2019 occurred between Nov. 15, 2018. While$ 612 was the nationwide average, it is essential to think about how monthly premiums change from state to state. While 39 states utilize the federal Healthcare Market, 12 states run their own markets, and data is not always reported for every state. Market Average Premiums and Average Advanced Premium Tax Credit( APTC) Area Average Premium Average Premium After APTC United States$ 612$ 143 Alabama$ 669$ 123 Alaska$ 746$ 174 Arizona$ 596$ 195 Arkansa$ 513$ 173 California$ 582 $168 Colorado$ 710$.
240 Connecticut $625 $264 Delaware$ 842 $202 District of Columbia$ 469 $447 Florida$ 605$ 100 Georgia$ 598$ 127 Hawaii$ 664 $214 Idaho N/A Substance Abuse Center N/A Illinois$ 646 $207 Indiana $491$ 259 Iowa$ Drug Abuse Treatment 918$ 126 Kansas $661$ 149 Kentucky $595 $196 Louisiana $613 $182 Maine$ 675$ 155 Maryland $552 $191 Massachusetts$ 392$ 204 Michigan $498$ 171 Minnesota$ 455$ 279 Mississippi $641 $76 Missouri$ 645$ 158 Montana$ 670 $174 Nebraska$ 866 $80 Nevada$ 509 $152 New Hampshire $540 $237 New Jersey $511 $235 New Mexico $483 $174 New york city $618 $224 North Carolina $729 $114 North Dakota $502 $165 Ohio $538 $234 Oklahoma $674 $77 Oregon $560 $222 Pennsylvania $654 $193 Rhode Island $443 $174 South Carolina $669 $116 South Dakota $652 $137 Tennessee $659 $141 Texas $544 $118 Utah $459 $82 Vermont $573 $148 Virginia $687 $175 Washington $551 $286 West Virginia $937 $265 Wisconsin $700 $161 Wyoming $960 $125 Employer-sponsored health insurance strategy costs are trending upwards. The cost of family protection has increased 22% since 2014. When it concerns the expense of employer-sponsored health insurance, you require to consider that your company might contribute to the expense of your strategy as part of your staff member benefits. While the typical expense of a household strategy is $20,576, the data shows that employees are only paying about $6,015 per year, and the employer is paying the rest. You should likewise make between 100% and 400% of the Federal Poverty Line( FPL), or get approved for Medicare, Medicaid, Kid's Health.
The smart Trick of How Did The Patient Protection And Affordable Care Act Increase Access To Health Insurance? That Nobody is Talking About
Insurance Coverage Program, or other forms of public support. In the 48 adjoining United States( omitting Alaska and Hawaii )the FPL is$ 48,560 for an individual or$ 100,400 for a family of four. If you do not receive an aid, the percentage of your income you require to cover your health insurance expenses rises considerably. Health insurance coverage rates also increase by age. The Kaiser Family Foundation discovered that in 21 %of U.S. counties, individuals with a$ 50,000 wage would pay a different percentage for medical insurance due to the fact that of their age: If they were 27, they would pay about 7% of their earnings for the lowest-cost plan nationallyIf they were 40, they would need to pay more than 10 %of their income If they were 60, they would pay 17% of their.

income for the same strategy Now that you understand the typical costs of medical insurance and how to get approved for an aid, the concern you may have is: What is going to make the cost of your health insurance coverage increase or down? Aspects that will impact your expense of health insurance may consist of: If you qualify for an aid or notYour ageWhere you liveHow many people are covered by the plan (specific vs.
The 4-Minute Rule for How To Choose Network Doctors For Health Care Palns By Services
This is based on danger pooling. The social health insurance coverage design is also referred to as the Bismarck Model, after Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, who presented the very first universal healthcare system in Germany in the 19th century. The funds generally contract with a mix of public and private suppliers for the provision of a defined advantage plan.
Within social medical insurance, a number of functions may be carried out by parastatal or non-governmental sickness funds, or in a couple of cases, by private medical insurance companies. Social medical insurance is used in a variety of Western European nations and increasingly in Eastern Europe as well as in Israel and Japan.

Private insurance includes policies sold by business for-profit firms, non-profit business and neighborhood health insurers. Usually, personal insurance is voluntary in contrast to social insurance programs, which tend to be compulsory. In some countries with universal protection, private insurance frequently excludes certain health conditions that are expensive and the state healthcare system can provide protection.
In the United States, dialysis treatment for end stage kidney failure is usually paid for by federal government and not by the insurance coverage market. Those with privatized Medicare (Medicare Advantage) more info are the exception and should get their dialysis spent for through their insurer. Nevertheless, those with end-stage kidney failure generally can not purchase Medicare Benefit strategies - what is the affordable health care act.
The Preparation Commission of India has likewise recommended that the nation should accept insurance to attain universal health coverage. General tax revenue is currently used to meet the important health requirements of all people. A particular kind of personal medical insurance that has often emerged, if monetary risk security mechanisms have just a restricted effect, is community-based health insurance.

Contributions are not risk-related and there is typically a high level of neighborhood involvement in the running of these plans. Universal health care systems differ according to the degree of government involvement in providing care or medical insurance. In some countries, such as Canada, the UK, Spain, Italy, Australia, and the Nordic nations, the federal government has a high degree of involvement in the commissioning or shipment of health care services and gain access to is based upon residence rights, not on the purchase of insurance.
In some cases, the health funds are obtained from a mixture of insurance premiums, salary-related necessary contributions by workers or companies to managed illness funds, and by federal government taxes. These insurance coverage based systems tend to compensate personal or public medical companies, typically at heavily managed rates, through shared or openly owned medical insurance providers.
Based On The Foundations Of Federalism Fundamentals Explained
Universal healthcare is a broad idea that has been carried out in a number of methods. The typical denominator for all such programs is some kind of federal government action aimed at extending access to healthcare as widely as possible and setting minimum requirements. Most carry out universal health care through legislation, policy, and taxation.
Normally, some expenses are borne by the client at the time of consumption, however the bulk of costs originated from a mix of compulsory insurance and tax revenues. Some programs are paid for entirely out of tax incomes. In others, tax revenues are utilized either to money insurance coverage for the extremely poor or for those needing long-lasting persistent care.
This is a method of organising the shipment, and designating resources, of health care (and potentially social care) based https://gumroad.com/raseiswbte/p/some-ideas-on-in-nc-what-are-rules-for-integrated-care-of-both-medical-and-mental-health-services-you-should-know upon populations in an offered location with a typical need (such as asthma, end of life, immediate care). Instead of focus on institutions such as medical facilities, primary care, community care etc. the system focuses on the population with a typical as a whole.
where there is health injustice). This technique encourages integrated care and a more reliable use of resources. The United Kingdom National Audit Workplace in 2003 published an international contrast of 10 various healthcare systems in 10 developed nations, nine universal systems against one non-universal system (the United States), and their relative expenses and key health outcomes.
In some cases, federal government involvement also includes directly managing the health care system, however numerous nations use blended public-private systems to provide universal healthcare. World Health Company (November 22, 2010). Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-156402-1. Retrieved April 11, 2012. " Universal health protection (UHC)". Retrieved November 30, 2016. Matheson, Don * (January 1, 2015).
International Journal of Health Policy and Management. 4 (1 ): 4951. doi:10.15171/ ijhpm. 2015.09. PMC. PMID 25584354. Abiiro, Gilbert Abotisem; De Allegri, Manuela (July 4, 2015). " Universal health coverage from multiple perspectives: a synthesis of conceptual literature and international arguments". BMC International Health and Person Rights. 15: 17. doi:10.1186/ s12914-015-0056-9. ISSN 1472-698X.
PMID 26141806. " Universal health coverage (UHC)". World Health Organization. December 12, 2016. Recovered September 14, 2017. Rowland, Diane; Telyukov, Alexandre V. (Fall 1991). " Soviet Health Care From 2 Viewpoints" (PDF). Health Affairs. 10 (3 ): 7186. doi:10.1377/ hlthaff. 10.3.71. PMID 1748393. "OECD Reviews of Health Systems OECD Reviews of Health Systems: Russian Federation 2012": 38.
The 8-Minute Rule for Based On The Foundations Of Federalism
" Social welfare; Social security; Benefits in kind; National health schemes". The new Encyclopdia Britannica (15th ed.). Chicago: Encyclopdia Britannica. ISBN 978-0-85229-443-7. Retrieved September 30, 2013. Richards, Raymond (1993 ). " 2 Social Security Acts". Closing the door to destitution: the shaping of the Social Security Acts of the United States and New Zealand.
p. 14. ISBN 978-0-271-02665-7. Obtained March 11, 2013. Mein Smith, Philippa (2012 ). " Making New Zealand 19301949". A succinct history of New Zealand (second ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 16465. ISBN 978-1-107-40217-1. Recovered March 11, 2013. Serner, Uncas (1980 ). "Swedish health legislation: turning points in reorganisation click here since 1945". In Heidenheimer, Arnold J.; Elvander, Nils; Hultn, Charly (eds.).
New York City: St. Martin's Press. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-312-71627-1. Universal and detailed health insurance was disputed at intervals all through the Second World War, and in 1946 such an expense was voted in Parliament. For financial and other factors, its promulgation was delayed till 1955, at which time coverage was extended to consist of drugs and illness payment, also.
( September 1, 2004). " The developmental well-being state in Scandinavia: lessons to the developing world". Geneva: United Nations Research Institute for Social Development. p. 7. Retrieved March 11, 2013. Evang, Karl (1970 ). Health services in Norway. English version by Dorothy Burton Skrdal (3rd ed.). Oslo: Norwegian Joint Committee on International Social Policy.
23. OCLC 141033. Considering that 2 July 1956 the whole population of Norway has been consisted of under the required health nationwide insurance program. Gannik, Dorte; Holst, Erik; Wagner, Mardsen (1976 ). "Main health care". The nationwide health system in Denmark. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health. pp. 4344. hdl:2027/ pur1.32754081249264. Alestalo, Matti; Uusitalo, Hannu (1987 ).
In Plants, Peter (ed.). Development to limitations: the Western European well-being states since The second world war, Vol. 4 Appendix (run-throughs, bibliographies, tables). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. pp. 13740. ISBN 978-3-11-011133-0. Obtained March 11, 2013. Taylor, Malcolm G. (1990 ). "Saskatchewan healthcare insurance". Insuring national healthcare: the Canadian experience. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
96130. ISBN 978-0-8078-1934-0. Maioni, Antonia (1998 ). " The 1960s: the political battle". Parting at the crossroads: the emergence of health insurance in the United States and Canada. Princeton: Princeton University Press. pp. 12122. ISBN 978-0-691-05796-5. Retrieved September 30, 2013. Kaser, Michael (1976 ). "The USSR". Health care in the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe.
9 Easy Facts About How Does Usa Pay For Rehabilitation Health Care Services Explained
This is based on danger pooling. The social medical insurance model is likewise referred to as the Bismarck Design, after Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, who presented the very first universal healthcare system in Germany in the 19th century. The funds usually contract with a mix of public and private companies for the arrangement of a specified benefit package.
Within social health insurance coverage, a number of functions might be executed by parastatal or non-governmental illness funds, or in a couple of cases, by private health insurance coverage business. Social health insurance is utilized in a variety of Western European countries and progressively in Eastern Europe as well as in Israel and Japan.
Private insurance coverage consists of policies sold by commercial for-profit firms, non-profit business and community health insurance providers. Typically, personal insurance is voluntary in contrast to social insurance coverage programs, which tend to be required. In some countries with universal coverage, personal insurance often leaves out particular health conditions that are pricey and the state healthcare system can provide protection.
In the United States, dialysis treatment for end stage renal failure is normally paid for by federal government and not by the insurance coverage industry. Those with privatized Medicare (Medicare Benefit) are the exception and needs to get their dialysis spent for through their insurance provider. However, those with end-stage kidney failure normally can not buy Medicare Advantage strategies - why is health care so expensive.
The Planning Commission of India has likewise suggested that the nation ought to embrace insurance to accomplish universal health coverage. General tax income is presently utilized to satisfy the necessary health requirements of all people. A specific type of private medical insurance that has often emerged, if monetary danger defense systems have only a limited impact, is community-based health insurance coverage.
Contributions are not risk-related and there is generally a high level of community involvement in the running of these strategies. Universal health care systems vary according to the degree of federal government participation in offering care or health insurance coverage. In some countries, such as Canada, the UK, Spain, Italy, Australia, and the Nordic nations, the federal government has a high degree of participation in the commissioning or delivery of health care services and gain access to is based upon house rights, not on the purchase of insurance coverage.
Sometimes, the health funds are derived from a mixture of insurance premiums, salary-related necessary contributions by staff members or employers to regulated illness funds, and by government taxes. These insurance based systems tend to compensate personal or public medical providers, often at heavily managed rates, through shared or openly owned medical insurance companies.
The Ultimate Guide To You Should Examine All Of The Following Except
Universal healthcare is a broad principle that has been executed in several methods. The typical denominator for all such programs is some type of federal government action focused on extending access to healthcare as commonly as possible and setting minimum requirements. Most carry out universal healthcare through legislation, guideline, and tax.
Typically, some expenses are borne by the patient at the time of intake, however the bulk of expenses originated from a combination of obligatory insurance and tax incomes. Some programs are spent for completely out of tax profits. In others, tax profits are utilized either to money insurance coverage for the very bad or for those requiring long-lasting chronic care.
This is a method of organising the delivery, and allocating resources, of healthcare (and potentially social care) based upon populations in a provided geography with a typical requirement (such as asthma, end of life, immediate care). Instead of concentrate on institutions such as health centers, medical care, neighborhood care and so on the system focuses on the population with a common as a whole.
where there is health inequity). This approach motivates incorporated care and a more efficient usage of resources. The United Kingdom National Audit Workplace in 2003 published a worldwide contrast of 10 different healthcare systems in 10 established nations, nine universal systems versus one non-universal system (the United States), and their relative costs and key health results.

In many cases, government involvement likewise consists of straight handling the healthcare system, however lots of countries utilize combined public-private systems to provide universal health care. World Health Organization (November more info 22, 2010). Geneva: World Health Company. ISBN 978-92-4-156402-1. Recovered April 11, 2012. " Universal health coverage (UHC)". Recovered November 30, 2016. Matheson, Don * (January 1, 2015).
International Journal of Health Policy and Management. 4 (1 ): 4951. doi:10.15171/ ijhpm. 2015.09. PMC. PMID 25584354. Abiiro, Gilbert Abotisem; De Allegri, Manuela (July 4, 2015). " Universal health protection from multiple viewpoints: a synthesis of conceptual literature and international disputes". BMC International Health and Person Rights. 15: 17. doi:10.1186/ s12914-015-0056-9. ISSN 1472-698X.
PMID 26141806. " Universal health coverage (UHC)". World Health Company. December 12, 2016. Retrieved September 14, 2017. Rowland, Diane; Telyukov, Alexandre V. (Fall 1991). " Soviet Health Care From Two Viewpoints" (PDF). Health Affairs. 10 (3 ): 7186. doi:10.1377/ hlthaff. 10.3.71. PMID 1748393. "OECD Reviews of Health Systems OECD Reviews of Health Systems: Russian Federation 2012": 38.
The Ultimate Guide To What Is Universal Health Care
" Social welfare; Social security; Benefits in kind; National health schemes". The brand-new Encyclopdia Britannica (15th ed.). Chicago: Encyclopdia Britannica. ISBN 978-0-85229-443-7. Recovered September 30, 2013. Richards, Raymond (1993 ). " Two Social Security Acts". Closing the door to destitution: the shaping of the Social Security Acts of the United States and New Zealand.
p. 14. ISBN 978-0-271-02665-7. Retrieved March 11, 2013. Mein Smith, Philippa (2012 ). " Making New Zealand 19301949". A succinct history of New Zealand (second ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 16465. ISBN 978-1-107-40217-1. Recovered March 11, 2013. Serner, Uncas (1980 ). "Swedish health legislation: turning points in reorganisation since 1945". In Heidenheimer, Arnold J.; Elvander, Nils; Hultn, Charly (eds.).
New York City: St. Martin's Press. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-312-71627-1. Universal and extensive health insurance was disputed at intervals all through the 2nd World War, and in 1946 such an expense was enacted Parliament. For financial and other factors, its promulgation was delayed up until 1955, at which time protection was extended to include drugs and illness compensation, too.
( September 1, 2004). " The developmental welfare state in Scandinavia: lessons to the establishing world". Geneva: United Nations Research Study Institute for Social Development. p. 7. Recovered March 11, 2013. Evang, Karl (1970 ). Health services in Norway. English variation by Dorothy Burton Skrdal (3rd click here ed.). Oslo: Norwegian Joint Committee on International Social Policy.
23. OCLC 141033. Given that 2 July 1956 the whole population of Norway has been included under the obligatory health nationwide insurance program. Gannik, Dorte; Holst, Erik; Wagner, Mardsen (1976 ). "Primary health care". The national health system in Denmark. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health. pp. 4344. hdl:2027/ pur1.32754081249264. Alestalo, Matti; Uusitalo, Hannu (1987 ).
In Plants, Peter (ed.). Growth to limitations: the Western European welfare states given that World War II, Vol. 4 Appendix (run-throughs, bibliographies, tables). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. pp. 13740. ISBN 978-3-11-011133-0. Recovered March 11, 2013. Taylor, Malcolm G. (1990 ). "Saskatchewan medical care insurance coverage". Guaranteeing national healthcare: the Canadian experience. Chapel Hill: https://gumroad.com/raseiswbte/p/some-ideas-on-in-nc-what-are-rules-for-integrated-care-of-both-medical-and-mental-health-services-you-should-know University of North Carolina Press.

96130. ISBN 978-0-8078-1934-0. Maioni, Antonia (1998 ). " The 1960s: the political battle". Parting at the crossroads: the introduction of medical insurance in the United States and Canada. Princeton: Princeton University Press. pp. 12122. ISBN 978-0-691-05796-5. Recovered September 30, 2013. Kaser, Michael (1976 ). "The USSR". Health care in the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe.
Our Analyze The Impact Of Technology On How Health Care Services Are Delivered In The Va Diaries
A student once took issue with him and when Dr. Sigerist asked him to quote his authority, the student yelled, "You yourself said so!" "When?" asked Dr. Sigerist. "3 years earlier," addressed the student. "Ah," stated Dr. Sigerist, "three years is a very long time. I've changed my mind ever since." I think for me this speaks with the altering tides of viewpoint which everything is in flux and open to renegotiation.
Much of this talk was paraphrased/annotated directly from the sources listed below, in particular the work of Paul Starr: Bauman, Harold, "Verging on National Medical Insurance since 1910" in Changing to National Healthcare: Ethical and Policy Issues (Vol. 4, Principles in an Altering World) edited by Heufner, Robert P. and Margaret # P.
" Increase President's Strategy", Washington Post, p. A23, February 7, 1992. Brown, Ted. "Isaac Max Rubinow", (a biographical sketch), American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1863-1864, 1997 Danielson, David A., and Arthur Mazer. "The Massachusetts Referendum for a National Health Program", Journal of Public Health Policy, Summertime 1986.

" The House of Falk: The Paranoid Design in American Home Politics", American Journal of Public Health", Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1836 1843, 1997. Falk, I (what is home health care).S. "Propositions for National Medical Insurance in the U.S.A.: Origins and Development and Some Viewpoints for the Future', Milbank Memorial Fund Quarterly, Health and Society, pp.
Gordon, Colin. "Why No National Health Insurance in the http://andersonbekt382.bearsfanteamshop.com/the-main-principles-of-surgical-site-infections-in-america-and-how-many-are-treated-in-home-health-care-services US? The Limits of Social Arrangement in War and Peace, 1941-1948", Journal of Policy History, Vol. 9, No (what is universal health care). 3, pp. 277-310, 1997. "History in a Tea Wagon", Time Magazine, No. 5, pp. 51-53, January 30, 1939. Marmor, Ted. "The History of Healthcare Reform", Roll Call, pp.

Navarro, Vicente. "Case history as a Validation Instead Of Description: Review of Starr's The Social Transformation of American Medication" International Journal of Health Solutions, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp. 511-528, 1984. Navarro, Vicente. "Why Some Nations Have National Medical Insurance, Others Have National Health Service, and the United States has Neither", International Journal of Health Providers, Vol.
Some Known Details About How Does Canadian Health Care Work
3, pp. 383-404, 1989. Rothman, David J. "A Century of Failure: Health Care Reform in America", Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law", Vol. 18, No. 2, Summer 1993. Rubinow, Isaac Max. "Labor Insurance Coverage", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1862 1863, 1997 (Initially released in Journal of Political Economy, Vol.
362-281, 1904). Starr, Paul. The Social Change of American Medication: The rise of a sovereign occupation and the making of a huge market. Basic Books, 1982. Starr, Paul. "Improvement in Defeat: The Altering Goals of National Medical Insurance, 1915-1980", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 72, No. 1, pp. 78-88, 1982 - how does universal health care work.
" Crisis and Change in America's Health System", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 63, No. 4, April 1973. "Towards a National Treatment System: II. The Historical Background", Editorial, Journal of Public Health Policy, Fall 1986. Trafford, Abigail, and Christine Russel, "Opening Night for Clinton's Plan", Washington Post Health Publication, pp.
The United States does not have universal health insurance coverage. Nearly 92 percent of the population was approximated to have coverage in 2018, leaving 27.5 million people, or 8.5 percent of the population, uninsured. 1 Motion toward protecting the right to health care has been incremental. 2 Employer-sponsored medical insurance was introduced during the 1920s.
In 2018, about 55 percent of the population was covered under employer-sponsored insurance coverage. 3 In 1965, the first public insurance programs, Medicare and Medicaid, were enacted through the Social Security Act, and others followed. Medicare. Medicare makes sure a universal right to health care for individuals age 65 and older. Eligible populations and the range of benefits covered have gradually expanded.
All recipients are entitled to standard Medicare, a Continue reading fee-for-service program that supplies medical facility insurance coverage (Part A) and medical insurance coverage (Part B). Given that 1973, beneficiaries have had the option to get their coverage through either traditional Medicare or Medicare Advantage (Part C), under which people enroll in a personal health upkeep organization (HMO) or managed care organization (how much is health care).
Some Ideas on Which Team Member Acts As A Liaison Between The Health Care Facility And The Media? You Need To Know
Medicaid. The Medicaid program first offered states the choice to receive federal matching funding for offering health care services to low-income families, the blind, and individuals with impairments. Protection was gradually made compulsory for low-income pregnant ladies and infants, and later for children as much as age 18. Today, Medicaid covers 17.9 percent of Americans.
People need to get Medicaid protection and to re-enroll and recertify annually. As of 2019, more than two-thirds of Medicaid beneficiaries were registered in handled care companies. 4 Children's Health Insurance Program. In 1997, the Children's Medical insurance Program, or CHIP, was produced as a public, state-administered program for children in low-income households that earn too much to receive Medicaid but that are not likely to be able to afford private insurance coverage.
5 In some states, it operates as an extension of Medicaid; in other states, it is a different program. Inexpensive Care Act. In 2010, the passage of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, or ACA, represented the biggest expansion to date of the federal government's role in financing and regulating healthcare.
The ACA led to an approximated 20 million acquiring coverage, decreasing the share of uninsured adults aged 19 to 64 from 20 percent in 2010 to 12 percent in 2018.6 The federal government's obligations include: setting legislation and national methods administering and spending for the Medicare program cofunding and setting basic requirements and policies for the Medicaid program cofunding CHIP funding health insurance for federal staff members as well as active and previous members of the military and their families managing pharmaceutical products and medical devices running federal markets for private medical insurance offering premium aids for personal marketplace protection.
The ACA established "shared responsibility" among federal government, companies, and people for ensuring that all Americans have access to cost effective and good-quality health insurance. The U.S. Department of Health and Person Providers is the federal government's principal agency included with healthcare services. The states cofund and administer their CHIP and Medicaid programs according to federal regulations.
They likewise help finance health insurance for state staff members, regulate personal insurance, and license health professionals. Some states also manage health insurance for low-income homeowners, in addition to Medicaid. In 2017, public spending accounted for 45 percent of overall health care spending, or around 8 percent of GDP. Federal costs represented 28 percent of total health care costs.
See This Report on When An Employee Takes Fmla Leave
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Providers is the largest governmental source of health protection financing. Medicare is financed through a combination of basic federal taxes, a mandatory payroll tax that pays for Part A (hospital insurance coverage), and private premiums. Medicaid is largely tax-funded, with federal tax profits representing two-thirds (63%) of costs, and state and local incomes the rest.
CHIP is moneyed through Go here matching grants provided by the federal government to states. The majority of states (30 in 2018) charge premiums under that program. Investing in personal medical insurance represented one-third (34%) of overall health expenses in 2018. Private insurance coverage is the main health coverage for two-thirds of Americans (67%).
Some Ideas on Who To Get Help From With Inadiquit Health Care Services You Need To Know
This is based on threat pooling. The social medical insurance design is also referred to as the Bismarck Design, after Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, who presented the first universal healthcare system in Germany in the 19th century. The funds normally contract with a mix of public and personal suppliers for the provision of a specified benefit bundle.
Within social medical insurance, a variety of functions may be executed by parastatal or non-governmental sickness funds, or in a few cases, by personal health insurance companies. Social medical insurance is used in a variety of Western European nations and increasingly in Eastern Europe along with in Israel https://gumroad.com/raseiswbte/p/some-ideas-on-in-nc-what-are-rules-for-integrated-care-of-both-medical-and-mental-health-services-you-should-know and Japan.
Personal insurance coverage consists of policies offered by business for-profit companies, non-profit companies and community health insurance providers. Usually, personal insurance is voluntary in contrast to social insurance programs, which tend to be required. In some nations with universal coverage, private insurance coverage often excludes specific health conditions that are expensive and the state healthcare system can provide protection.
In the United States, dialysis treatment for end phase kidney failure is normally spent for by government and not by the insurance coverage market. Those with privatized Medicare (Medicare Advantage) are the exception and should get their dialysis spent for through their insurer. However, those with end-stage kidney failure generally can not purchase Medicare Benefit plans - a health care professional is caring for a patient who is taking zolpidem.
The Planning Commission of India has also suggested that the nation must accept insurance coverage to attain universal health coverage. General tax profits is currently used to meet the important health requirements of all individuals. A specific kind of personal medical insurance that has frequently emerged, if monetary threat security mechanisms have only a minimal impact, is community-based medical insurance.
Contributions are not risk-related and there is generally a high level of community involvement in the running of these plans. Universal health care systems vary according to the degree of government participation in supplying care or health insurance. In some countries, such as Canada, the UK, Spain, Italy, Australia, and the Nordic nations, the federal government has a high degree of involvement in the commissioning or delivery of health care services and access is based on house rights, not on the purchase of insurance coverage.
Sometimes, the health funds are derived from a mix of insurance coverage premiums, salary-related necessary contributions by employees or companies to controlled illness funds, and by government taxes. These insurance coverage based systems tend to compensate private or public medical providers, typically at greatly controlled rates, through shared or openly owned medical insurers.
Our How Much Does Health Care Cost Statements
Universal health care is a broad concept that has been implemented in numerous methods. The common measure for all such programs is some form of federal government action focused on extending access to health care as commonly as possible and setting minimum standards. A lot of carry out universal healthcare through legislation, regulation, and taxation.
Normally, some costs are borne by the client at the time of usage, however the bulk of costs come from a mix of compulsory insurance and tax earnings. Some programs are paid for completely out of tax revenues. In others, tax revenues are used either to fund insurance for the really poor or for those requiring long-lasting chronic care.
This is a way of organising the shipment, and assigning resources, of health care (and possibly social care) based upon populations in a given geography with a common need (such as asthma, end of life, urgent care). Rather than focus on organizations such as hospitals, main care, community care and so on the system concentrates on the population with a typical as a whole.
where there is health injustice). This approach encourages integrated care and a more efficient use of resources. The UK National Audit Workplace in 2003 released a worldwide contrast of 10 different health care systems in ten established countries, nine universal systems against one non-universal system (the United States), and their relative costs and crucial health outcomes.
Sometimes, federal government participation likewise consists of directly managing the healthcare system, however many nations utilize blended public-private systems to deliver universal health care. World Health Company (November 22, 2010). Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN click here 978-92-4-156402-1. Recovered April 11, 2012. " Universal health coverage (UHC)". Recovered November 30, 2016. Matheson, Don * (January 1, 2015).
International Journal of Health Policy and Management. 4 (1 ): 4951. doi:10.15171/ ijhpm. 2015.09. PMC. PMID 25584354. Abiiro, Gilbert Abotisem; De Allegri, Manuela (July 4, 2015). " Universal health coverage from numerous point of views: a synthesis of conceptual literature and worldwide disputes". BMC International Health and Person Rights. 15: 17. doi:10.1186/ s12914-015-0056-9. ISSN 1472-698X.
PMID 26141806. " Universal health protection (UHC)". World Health Company. December 12, 2016. Retrieved September 14, 2017. Rowland, Diane; Telyukov, Alexandre V. (Fall 1991). " Soviet Healthcare From 2 Perspectives" (PDF). Health Affairs. 10 (3 ): 7186. doi:10.1377/ hlthaff. 10.3.71. PMID 1748393. "OECD Reviews of Health Systems OECD Evaluations of Health Systems: more info Russian Federation 2012": 38.
The Basic Principles Of Based On The Foundations Of Federalism
" Social welfare; Social security; Advantages in kind; National health plans". The brand-new Encyclopdia Britannica (15th ed.). Chicago: Encyclopdia Britannica. ISBN 978-0-85229-443-7. Obtained September 30, 2013. Richards, Raymond (1993 ). " 2 Social Security Acts". Closing the door to destitution: the shaping of the Social Security Acts of the United States and New Zealand.

p. 14. ISBN 978-0-271-02665-7. Recovered March 11, 2013. Mein Smith, Philippa (2012 ). " Making New Zealand 19301949". A succinct history of New Zealand (second ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 16465. ISBN 978-1-107-40217-1. Obtained March 11, 2013. Serner, Uncas (1980 ). "Swedish health legislation: milestones in reorganisation considering that 1945". In Heidenheimer, Arnold J.; Elvander, Nils; Hultn, Charly (eds.).
New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-312-71627-1. Universal and extensive health insurance was disputed at periods all through the Second World War, and in 1946 such a costs was voted in Parliament. For monetary and other reasons, its promulgation was postponed till 1955, at which time protection was encompassed include drugs and sickness compensation, too.

( September 1, 2004). " The developmental well-being state in Scandinavia: lessons to the developing world". Geneva: United Nations Research Study Institute for Social Development. p. 7. Obtained March 11, 2013. Evang, Karl (1970 ). Health services in Norway. English version by Dorothy Burton Skrdal (3rd ed.). Oslo: Norwegian Joint Committee on International Social Policy.
23. OCLC 141033. Since 2 July 1956 the whole population of Norway has actually been included under the obligatory health national insurance program. Gannik, Dorte; Holst, Erik; Wagner, Mardsen (1976 ). "Main health care". The national health system in Denmark. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health. pp. 4344. hdl:2027/ pur1.32754081249264. Alestalo, Matti; Uusitalo, Hannu (1987 ).
In Plants, Peter (ed.). Development to limits: the Western European welfare states considering that World War II, Vol. 4 Appendix (synopses, bibliographies, tables). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. pp. 13740. ISBN 978-3-11-011133-0. Obtained March 11, 2013. Taylor, Malcolm G. (1990 ). "Saskatchewan medical care insurance". Guaranteeing nationwide health care: the Canadian experience. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
96130. ISBN 978-0-8078-1934-0. Maioni, Antonia (1998 ). " The 1960s: the political battle". Parting at the crossroads: the emergence of medical insurance in the United States and Canada. Princeton: Princeton University Press. pp. 12122. ISBN 978-0-691-05796-5. Obtained September 30, 2013. Kaser, Michael (1976 ). "The USSR". Health care in the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe.
An Unbiased View of What Is Primary Care Health Services
A trainee as soon as took problem with him and when Dr. Sigerist asked him to quote his authority, the trainee yelled, "You yourself stated so!" "When?" asked Dr. Sigerist. "Three years ago," responded to the trainee. "Ah," said Dr. Sigerist, "3 years is a very long time. I've changed my mind ever since." I think for me this talks to the altering tides of opinion which whatever is in flux and open up to renegotiation.
Much of this talk was paraphrased/annotated directly from the sources listed below, in particular the work of Paul Starr: Bauman, Harold, "Bordering On National Medical Insurance considering that 1910" in Altering to National Healthcare: Ethical and Policy Issues (Vol. 4, Principles in an Altering World) modified by Heufner, Robert P. and Margaret # P.
" Increase President's Strategy", Washington Post, p. A23, February 7, 1992. Brown, Ted. "Isaac Max Rubinow", (a biographical sketch), American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1863-1864, 1997 Danielson, David A., and Arthur Mazer. "The Massachusetts Referendum for a National Health Program", Journal of Public Health Policy, Summer Season 1986.
" The House of Falk: The Paranoid Design in American Home Politics", American Journal of Public Health", Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1836 1843, 1997. Falk, I (who is eligible for care within the veterans health administration?).S. "Proposals for National Medical Insurance in the USA: Origins and Development and Some Perspectives for the Future', Milbank Memorial Fund Quarterly, Health and Society, pp.
Gordon, Colin. "Why No National Medical Insurance in the United States? The Limitations of Social Arrangement in War and Peace, 1941-1948", Journal of Policy Continue reading History, Vol. 9, No (how many countries have universal health care). 3, pp. 277-310, 1997. "History in a Tea Wagon", Time Magazine, No. 5, pp. 51-53, January 30, 1939. Marmor, Ted. "The History of http://andersonbekt382.bearsfanteamshop.com/the-main-principles-of-surgical-site-infections-in-america-and-how-many-are-treated-in-home-health-care-services Healthcare Reform", Roll Call, pp.
Navarro, Vicente. "Medical History as a Reason Instead Of Description: Review of Starr's The Social Transformation of American Medication" International Journal of Health Solutions, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp. 511-528, 1984. Navarro, Vicente. "Why Some Nations Have National Medical Insurance, Others Have National Health Service, and the United States has Neither", International Journal of Health Providers, Vol.
An Unbiased View of Which Type Of Health Care Facility Employs The Most People In The U.s.?
3, pp. 383-404, 1989. Rothman, David J. "A Century of Failure: Healthcare Reform in America", Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law", Vol. 18, No. 2, Summertime 1993. Rubinow, Isaac Max. "Labor Insurance", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1862 1863, 1997 (Originally published in Journal of Political Economy, Vol.
362-281, 1904). Starr, Paul. The Social Transformation of American Medication: The increase of a sovereign occupation and the making of a huge market. Standard Books, 1982. Starr, Paul. "Improvement in Defeat: The Altering Objectives of National Medical Insurance, 1915-1980", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 72, No. 1, pp. 78-88, 1982 - what home health care is covered by medicare.
" Crisis and Change in America's Health System", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 63, No. 4, April 1973. "Towards a National Treatment System: II. The Historic Background", Editorial, Journal of Public Health Policy, Fall 1986. Trafford, Abigail, and Christine Russel, "Opening Night for Clinton's Plan", Washington Post Health Magazine, pp.
The United States does not have universal health insurance coverage. Nearly 92 percent of the population was estimated to have protection in 2018, leaving 27.5 million people, or 8.5 percent of the population, uninsured. 1 Motion toward protecting the right to healthcare has actually been incremental. 2 Employer-sponsored medical insurance was introduced during the 1920s.
In 2018, about 55 percent of the population was covered under employer-sponsored insurance. 3 In 1965, the first public insurance coverage programs, Medicare and Medicaid, were enacted through the Social Security Act, and others followed. Medicare. Medicare makes sure a universal right to health care for persons age 65 and older. Eligible populations and the series of advantages covered have actually slowly expanded.
All recipients are entitled to conventional Medicare, a fee-for-service program that supplies health center insurance (Part A) and medical insurance coverage (Part B). Given that 1973, recipients have actually had the alternative to receive their coverage through either standard Medicare or Go here Medicare Benefit (Part C), under which people enroll in a private health care organization (HMO) or handled care company (how much is health care).
More About What Is Preventive Health Care
Medicaid. The Medicaid program initially gave states the choice to receive federal matching funding for offering healthcare services to low-income families, the blind, and individuals with disabilities. Protection was gradually made compulsory for low-income pregnant ladies and babies, and later for kids up to age 18. Today, Medicaid covers 17.9 percent of Americans.

Individuals require to obtain Medicaid coverage and to re-enroll and recertify each year. As of 2019, more than two-thirds of Medicaid beneficiaries were enrolled in managed care organizations. 4 Children's Health Insurance coverage Program. In 1997, the Kid's Health Insurance coverage Program, or CHIP, was produced as a public, state-administered program for kids in low-income families that make too much to qualify for Medicaid but that are not likely to be able to afford personal insurance.
5 In some states, it runs as an extension of Medicaid; in other states, it is a different program. Affordable Care Act. In 2010, the passage of the Client Protection and Affordable Care Act, or ACA, represented the biggest expansion to date of the federal government's function in financing and controling health care.
The ACA led to an estimated 20 million gaining coverage, reducing the share of uninsured adults aged 19 to 64 from 20 percent in 2010 to 12 percent in 2018.6 The federal government's responsibilities consist of: setting legislation and national strategies administering and paying for the Medicare program cofunding and setting standard requirements and guidelines for the Medicaid program cofunding CHIP funding medical insurance for federal employees in addition to active and past members of the military and their households regulating pharmaceutical products and medical gadgets running federal markets for private medical insurance offering premium subsidies for private marketplace coverage.
The ACA established "shared duty" amongst government, companies, and individuals for ensuring that all Americans have access to economical and good-quality health insurance coverage. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Being Services is the federal government's principal agency included with healthcare services. The states cofund and administer their CHIP and Medicaid programs according to federal policies.
They likewise help fund medical insurance for state staff members, manage personal insurance coverage, and license health specialists. Some states also manage health insurance coverage for low-income residents, in addition to Medicaid. In 2017, public spending accounted for 45 percent of overall healthcare costs, or roughly 8 percent of GDP. Federal spending represented 28 percent of total health care spending.
Why Did Democrats Block Veterans Health Care Bill Fundamentals Explained
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Solutions is the biggest governmental source of health coverage funding. Medicare is financed through a mix of general federal taxes, a mandatory payroll tax that pays for Part A (health center insurance coverage), and private premiums. Medicaid is largely tax-funded, with federal tax revenues representing two-thirds (63%) of expenses, and state and regional profits the rest.
CHIP is funded through matching grants offered by the federal government to states. The majority of states (30 in 2018) charge premiums under that program. Investing in private medical insurance accounted for one-third (34%) of overall health expenditures in 2018. Private insurance coverage is the primary health coverage for two-thirds of Americans (67%).
The 9-Second Trick For What Is More Affordable Urgent Care Metro Urgent Care Or Concentra Health Services
A trainee as soon as differed with him and when Dr. Sigerist asked him to estimate his authority, the student yelled, "You yourself said so!" "When?" asked Dr. Sigerist. "Three years earlier," responded to the trainee. "Ah," said Dr. Sigerist, "3 years is a long period of time. I have actually altered my mind ever since." I think for me this talks to the changing tides of viewpoint and that everything is in flux and available to renegotiation.
Much of this talk was paraphrased/annotated straight from the sources listed below, in specific the work of Paul Starr: Bauman, Harold, "Bordering On National Health Insurance since 1910" in Altering to National Healthcare: Ethical and Policy Issues (Vol. 4, Ethics in a Changing World) modified by Heufner, Robert P. and Margaret # P.

" Increase President's Plan", Washington Post, p. A23, February 7, 1992. Brown, Ted. "Isaac Max Rubinow", (a biographical sketch), American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1863-1864, 1997 Danielson, David A., and Arthur Mazer. "The Massachusetts Referendum for a National Health Program", Journal of Public Health Policy, Summer Season 1986.
" The House of Falk: The Paranoid Style in American Home Politics", American Journal of Public Health", Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1836 1843, 1997. Falk, I (which countries have universal health care).S. "Proposals Continue reading for National Health Insurance Coverage in the USA: Origins and Development and Some Point Of Views for the Future', Milbank Memorial Fund Quarterly, Health and Society, pp.
Gordon, Colin. "Why No National Medical Insurance in the United States? The Limits of Social Provision in War and Peace, 1941-1948", Journal of Policy History, Vol. 9, No (what is the affordable health care act). 3, pp. 277-310, 1997. "History in a Tea Wagon", Time Publication, No. 5, pp. 51-53, January 30, 1939. Marmor, Ted. "The History of Health Care Reform", Roll Call, pp.
Navarro, Vicente. "Case history as a Justification Rather than Description: Critique of Starr's The Social Improvement of American Medication" International Journal of Health Solutions, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp. 511-528, 1984. Navarro, Vicente. "Why Some Nations Have National Health Insurance, Others Have National Health Service, and the United States has Neither", International Journal of Health Solutions, Vol.
What Is A Health Care Spending Account Fundamentals Explained
3, pp. 383-404, 1989. Rothman, David J. "A Century of Failure: Health Care Reform in America", Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law", Vol. 18, No. 2, Summer 1993. Rubinow, Isaac Max. "Labor Insurance", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1862 1863, 1997 (Originally published in Journal of Political Economy, Vol.
362-281, 1904). Starr, Paul. The Social Transformation of American Medicine: The rise of a sovereign occupation and the making of a vast industry. Basic Books, 1982. Starr, Paul. "Transformation in Defeat: The Changing Goals of National Health Insurance Coverage, 1915-1980", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 72, No. 1, pp. 78-88, 1982 - what is single payer health care.
" Crisis and Change in America's Health System", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 63, No. 4, April 1973. "Toward a National Healthcare System: II. The Historical Background", Editorial, Journal of Public Health Policy, Fall 1986. Trafford, Abigail, and Christine Russel, "Opening Night for Clinton's Plan", Washington Post Health Magazine, pp.
The United States does not have universal health insurance protection. Almost 92 percent of the population was approximated to have protection in 2018, leaving 27.5 million people, or 8.5 percent of the population, uninsured. 1 Movement towards protecting the right to healthcare has been incremental. 2 Employer-sponsored health insurance was introduced throughout the 1920s.
In 2018, about 55 percent of the population was covered under employer-sponsored insurance. 3 In 1965, the first public insurance programs, Medicare and Medicaid, were enacted through the Social Security Act, and others followed. Medicare. Medicare makes sure a universal right to health care for individuals age 65 and older. Eligible populations and the series of advantages covered have actually gradually expanded.
All recipients are entitled to standard Medicare, a fee-for-service program that supplies healthcare facility insurance (Part A) and medical insurance (Part B). Given that 1973, beneficiaries have actually had the option to receive their protection through either standard Medicare or Medicare Advantage (Part C), under http://andersonbekt382.bearsfanteamshop.com/the-main-principles-of-surgical-site-infections-in-america-and-how-many-are-treated-in-home-health-care-services which individuals register in a personal health care company (HMO) or managed care organization (what does a health care administration do).
8 Easy Facts About Why Is Health Care So Expensive Shown
Medicaid. The Medicaid program initially offered states the choice to receive federal matching financing for providing healthcare services to low-income households, the blind, and individuals with specials needs. Coverage was slowly made compulsory for low-income pregnant ladies and babies, and later for children approximately age 18. Today, Medicaid covers 17.9 percent of Americans.
People need to obtain Medicaid coverage and to re-enroll and recertify each year. As of 2019, more than two-thirds of Medicaid beneficiaries were registered in managed care companies. 4 Children's Health Insurance coverage Program. In 1997, the Kid's Medical insurance Program, or CHIP, was produced as a public, state-administered program for children in low-income households that make too much to receive Medicaid however that are not likely to be able to manage personal insurance coverage.
5 In some states, it runs as an extension of Medicaid; in other states, it is a separate program. Inexpensive Care Act. In 2010, the passage of the Patient Defense and Affordable Care Act, or ACA, represented the largest expansion to date of the federal government's function in funding and controling health care.
The ACA led to an estimated 20 million gaining protection, lowering the share of uninsured grownups aged 19 to 64 from 20 percent in 2010 to 12 percent in 2018.6 The federal government's duties consist Go here of: setting legislation and nationwide methods administering and paying for the Medicare program cofunding and setting standard requirements and policies for the Medicaid program cofunding CHIP financing medical insurance for federal workers along with active and past members of the military and their households controling pharmaceutical products and medical gadgets running federal marketplaces for personal health insurance providing premium aids for personal market protection.
The ACA developed "shared obligation" among government, employers, and individuals for making sure that all Americans have access to affordable and good-quality health insurance coverage. The U.S. Department of Health and Person Providers is the federal government's primary agency included with health care services. The states cofund and administer their CHIP and Medicaid programs according to federal guidelines.
They likewise help finance medical insurance for state staff members, control private insurance coverage, and license health specialists. Some states likewise handle health insurance coverage for low-income homeowners, in addition to Medicaid. In 2017, public costs accounted for 45 percent of total health care costs, or approximately 8 percent of GDP. Federal spending represented 28 percent of overall health care spending.
6 Simple Techniques For What Is A Single Payer Health Care System
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Solutions is the largest governmental source of health coverage financing. Medicare is funded through a mix of general federal taxes, a compulsory payroll tax that pays for Part A (healthcare facility insurance), and individual premiums. Medicaid is mainly tax-funded, with federal tax incomes representing two-thirds (63%) of costs, and state and local earnings the remainder.
CHIP is moneyed through matching grants offered by the federal government to states. The majority of states (30 in 2018) charge premiums under that program. Investing in personal health insurance coverage represented one-third (34%) of total health expenses in 2018. Private insurance is the main health coverage for two-thirds of Americans (67%).
Fascination About Who Is In Charge Of The Los Angeles County Of Health Care Services
The population of Tamil Nadu has actually significantly benefited, for example, from its splendidly run mid-day meal service in schools and from its substantial system of nutrition and health care of pre-school children. The message that striking rewards can be enjoyed from serious efforts at institutingor even moving towardsuniversal healthcare is tough to miss out on.
Maybe most notably, it suggests including ladies in the shipment of health and education in a much bigger method than is normal in the developing world. The question can, however, be asked: how does universal health care become economical in poor countries? Undoubtedly, how has UHC been afforded in those countries or states that have run versus the widespread and established belief that a bad nation must first grow abundant prior to it is able to fulfill the costs of healthcare for all? The alleged sensible argument that if a country is bad it can not provide UHC is, however, based on crude and faulty economic thinking (which of the following are characteristics of the medical care determinants of health?).
A poor country might have less cash to invest in healthcare, but it also needs to spend less to provide the very same labour-intensive services (far less than what a richerand higher-wageeconomy would need to pay). Not to take into consideration the ramifications of large wage distinctions is a gross oversight that distorts the conversation of the price of labour-intensive activities such as healthcare and education in low-wage economies.
Given the extremely unequal distribution of incomes in lots of economies, there can be severe inefficiency as well as unfairness in leaving the circulation of healthcare entirely to people's particular capabilities to buy medical services. UHC can produce not just higher equity, however likewise much larger total health accomplishment for the nation, because the remedying of a lot of the most easily curable illness and the prevention of readily avoidable disorders get left out under the out-of-pocket system, due to the fact that of the failure of the bad to afford even extremely primary health care and medical attention.
This is not to deny that fixing inequality as much as possible is a crucial valuea topic on which I have edited numerous years. Reduction of financial and social inequality likewise has instrumental relevance for excellent health. Conclusive proof of this is provided in the work of Michael Marmot, Richard Wilkinson and others on the "social factors of health", revealing that gross inequalities damage the health of the underdogs of society, both by undermining their lifestyles and by making them prone to harmful behaviour patterns, such as smoking cigarettes and extreme drinking.

Healthcare for all can be carried out with relative ease, and it would be an embarassment to delay its accomplishment until such time as it can be combined with the more intricate and challenging goal of getting rid of all inequality. Third, numerous medical and health services are shared, instead of being specifically utilized by each specific individually.

The Best Strategy To Use For What Countries Have Single Payer Get more info Health Care
Health care, hence, has strong parts of what in economics is called a "collective great," which usually is extremely inefficiently assigned by the pure market system, as has been thoroughly discussed by economists such as Paul Samuelson. Covering more people together can sometimes cost less than covering a smaller number separately.
Universal coverage prevents their spread and cuts expenses through better epidemiological care. This point, as used to individual regions, has actually been identified for a long time. The conquest of epidemics has, in fact, been attained by not leaving anyone without treatment in regions where the spread of infection is being taken on.
Right now, the pandemic of Ebola is triggering alarm even in parts of the world far away from its place of origin in west Africa. For example, the US has actually taken numerous pricey steps to prevent the spread of Ebola within its own borders. Had there been reliable UHC in the nations of origin of the disease, this issue could have been reduced or perhaps eliminated (what is a single payer health care system).
The estimation of the supreme financial expenses and advantages of healthcare can be an even more complex procedure than the universality-deniers would have us think. In the lack of a fairly well-organised system of public healthcare for all, numerous individuals are afflicted by expensive and inefficient private healthcare (how does electronic health records improve patient care). As has been evaluated by numerous economic experts, most notably Kenneth Arrow, there can not be a well-informed competitive market balance in the field of medical attention, because of what economic experts call "asymmetric information".
Unlike in the market for numerous products, such as t-shirts or umbrellas, the buyer of medical treatment understands far less than what the seller the doctordoes, and this vitiates the performance of market competition. This applies to the marketplace for health insurance coverage also, considering that insurer can not completely understand what patients' health conditions are.
And there is, in addition, the much larger issue that private insurance business, if unrestrained by regulations, have a strong financial interest in excluding patients who are required "high-risk". So one way or another, the government needs to play an active part in making UHC work. The issue of uneven details applies to the shipment of medical services itself.
The 6-Second Trick For Who Led The Reform Efforts For Mental Health Care In The United States?
And when medical workers are scarce, so that there is not much competition either, it can make the predicament of the buyer of medical treatment even worse. Furthermore, when the supplier of health care is not himself trained (as is typically the case in numerous nations with lacking health systems), the circumstance worsens still.
In some countriesfor example Indiawe see both systems running side by side in various states within the country. A state such as Kerala supplies fairly reputable Click here for more basic healthcare for all through public servicesKerala pioneered UHC in India a number of years earlier, through substantial public health services. As the population of Kerala has actually grown richerpartly as a result of universal health care and near-universal literacymany individuals now pick to pay more and have additional personal health care.
In contrast, states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh provide abundant examples of exploitative and inefficient healthcare for the bulk of the population. Not remarkably, people who reside in Kerala live a lot longer and have a much lower incidence of preventable diseases than do people from states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh.
In the lack of organized look after all, illness are typically permitted to develop, that makes it much more pricey to treat them, often including inpatient treatment, such as surgery. Thailand's experience clearly demonstrates how the need for more costly procedures might decrease greatly with fuller coverage of preventive care and early intervention.
If the development of equity is among the rewards of well-organised universal health care, improvement of efficiency in medical attention is certainly another. The case for UHC is often ignored because of insufficient gratitude of what well-organised and inexpensive health care for all can do to improve and enhance human lives.
In this context it is likewise needed to bear in mind a crucial tip contained in Paul Farmer's book Pathologies of Power: Health, Human being Rights and the New War on the Poor: "Claims that we reside in an era of minimal resources stop working to point out that these resources take place to be less minimal now than ever before in human history.
The 5-Second Trick For How Do You Qualify For Home Health Care Services?
The population of Tamil Nadu has considerably benefited, for example, from its splendidly run mid-day meal service in schools and from its comprehensive system of nutrition and health care of pre-school children. The message that striking benefits can be enjoyed from serious efforts at institutingor even moving towardsuniversal health care is tough to miss.
Maybe most notably, it indicates including women in the shipment of health and education in a much bigger method than is normal in the establishing world. The question can, nevertheless, be asked: how does universal healthcare ended up being budget-friendly in poor nations? Indeed, how has UHC been managed in those nations or states that have run versus the extensive and entrenched belief that a poor nation must initially grow rich prior Click here for more to it is able to fulfill the expenses of healthcare for all? The supposed common-sense argument that if a country is poor it can not offer UHC is, however, based upon crude and defective financial reasoning (how much do home health care agencies charge).
A poor nation might have less money to spend on health care, however it likewise requires to invest less to offer the same labour-intensive services (far less than what a richerand higher-wageeconomy would need to pay). Not to consider the ramifications of large wage differences is a gross oversight that misshapes the conversation of the price of labour-intensive activities such as healthcare and education in low-wage economies.
Provided the hugely unequal distribution of earnings in many economies, there can be severe inefficiency as well as unfairness in leaving the distribution of health care totally to people's respective abilities to purchase medical services. UHC can produce not just higher equity, but also much larger general health accomplishment for the country, given that the remedying of numerous of the most quickly treatable diseases and the prevention of easily avoidable disorders get excluded under the out-of-pocket system, due to the fact that of the inability of the bad to manage even very elementary healthcare and medical attention.
This is not to deny that treating inequality as much as possible is a crucial valuea subject on which I have edited lots of years. Reduction of economic and social inequality likewise has critical importance for good health. Conclusive proof of this is offered in the work of Michael Marmot, Richard Wilkinson and others on the "social factors of health", revealing that gross inequalities hurt the health of the underdogs of society, both by undermining their way of lives and by making them vulnerable to hazardous behaviour patterns, such as smoking and extreme drinking.
Healthcare for all can be implemented with relative ease, and it would be an embarassment to delay its accomplishment till such time as it can be integrated with the more complex and hard goal of getting rid of all inequality. Third, many medical and health services are shared, instead of being specifically used by each specific individually.
Fascination About What Is Universal Health Care
Health care, therefore, has strong parts of what in economics is called a "collective good," which generally is really inefficiently assigned by the pure market system, as has been extensively discussed by financial experts such as Paul Samuelson. Covering more individuals together can often cost less than covering a smaller number separately.
Universal coverage prevents their spread and cuts expenses through much better epidemiological care. This point, as applied to individual areas, has Get more info been recognised for a long time. The conquest of epidemics has, in truth, been attained by not leaving anybody without treatment in regions where the spread of infection is being taken on.
Right now, the pandemic of Ebola is causing alarm even in parts of the world far from its location of origin in west Africa. For example, the US has taken many costly steps to prevent the spread of Ebola within its own borders. Had actually there been efficient UHC in the nations of origin of the illness, this issue might have been mitigated or even gotten rid of (when does senate vote on health care bill).
The calculation of the ultimate economic expenses and advantages of health care can be a much more complicated procedure than the universality-deniers would have us believe. In the lack of a reasonably well-organised system of public health care for all, lots of people are affected by expensive and inefficient personal health care (a health care professional is caring for a patient who is taking zolpidem). As has been analysed by numerous economists, most notably Kenneth Arrow, there can not be an educated competitive market stability in the field of medical attention, because of what economists call "uneven details".
Unlike in the market for lots of commodities, such as t-shirts or umbrellas, the purchaser of medical treatment knows far less than what the seller the doctordoes, and this vitiates the performance of market competition. This uses to the marketplace for health insurance coverage too, given that insurance companies can not completely understand what clients' health conditions are.

And there is, in addition, the much larger issue that personal insurance business, if unrestrained by regulations, have a strong financial interest in omitting clients who are required "high-risk". So one method or another, the government has to play an active part in making UHC work. The problem of uneven details applies to the shipment of medical services itself.
All About Who Is Eligible For Care Within The Veterans Health Administration
And when medical personnel are scarce, so that there is very little competitors either, it can make the dilemma of the buyer of medical treatment even worse. Additionally, when the provider of healthcare is not himself qualified (as is often the case in many nations with deficient health systems), the circumstance worsens still.
In some countriesfor example Indiawe see both systems running side by side in various states within the country. A state such as Kerala provides fairly trusted fundamental health care for all through public servicesKerala pioneered UHC in India numerous decades ago, through comprehensive public health services. As the population of Kerala has grown richerpartly as an outcome of universal healthcare and near-universal literacymany people now pick to pay more and have additional personal healthcare.
In contrast, states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh provide numerous examples of exploitative and ineffective healthcare for the bulk of the population. Not surprisingly, individuals who live in Kerala live a lot longer and have a much lower occurrence of avoidable illnesses than do individuals from states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh.
In the absence of systematic look after all, diseases are typically permitted to establish, which makes it a lot more costly to treat them, typically involving inpatient treatment, such as surgical treatment. Thailand's experience plainly shows how the need for more costly treatments may go down greatly with fuller protection of preventive care and early intervention.
If the advancement of equity is among the rewards of well-organised universal healthcare, improvement of performance in medical attention is certainly another. The case for UHC is often ignored due to the fact that of insufficient appreciation of what well-organised and cost effective health care for all can do to enrich and enhance human lives.
In this context it is also needed to keep in mind a crucial reminder contained in Paul Farmer's book Pathologies of Power: Health, Human Rights and the New War on the Poor: "Claims that we reside in an age of minimal resources fail to mention that these resources occur to be less minimal now than ever prior to in human history.
Fascination About What Effects Will Changing Population Demographics Have On Health Care Costs And Services
The population of Tamil Nadu has actually considerably benefited, for example, from its splendidly run mid-day meal service in schools and from its extensive system of nutrition and healthcare of pre-school children. The message that striking rewards can be gained from severe attempts at institutingor even moving towardsuniversal healthcare is hard to miss.
Maybe most notably, it means including females in the delivery of health and education in a much bigger way than is usual in the establishing world. The question can, nevertheless, be asked: how does universal health care become budget-friendly in bad nations? Undoubtedly, how has UHC been paid for in those countries or states that have run against the widespread and established belief that a bad nation must initially grow abundant before it is able to fulfill the costs of health care for all? The supposed sensible argument that if a nation is poor it can not supply UHC is, however, based on crude and faulty economic reasoning (who is eligible for care within the veterans health administration).
A Get more info poor nation may have less cash to invest in healthcare, but it also requires to invest less to offer the exact same labour-intensive services (far less than what a richerand higher-wageeconomy would have to pay). Not to take into account the ramifications of large wage differences is a gross oversight that distorts the conversation of the affordability of labour-intensive activities such as health care and education in low-wage economies.
Provided the hugely unequal circulation of incomes in many economies, there can be severe ineffectiveness in addition to unfairness in leaving the distribution of healthcare totally to people's particular abilities to buy medical services. UHC can bring about not only higher equity, however likewise much larger overall health accomplishment for the country, because the remedying of much of the most easily curable illness and the avoidance of readily preventable conditions get overlooked under the out-of-pocket system, since of the failure of the poor to pay for even extremely primary healthcare and medical attention.
This is not to deny that correcting inequality as much as possible is an essential valuea subject on which I have actually edited lots of years. Decrease of economic and social inequality likewise has critical relevance for good health. Definitive proof of this is provided in the work of Michael Marmot, Richard Wilkinson and others on the "social factors of health", showing that gross inequalities hurt the health of the underdogs Click here for more of society, both by weakening their lifestyles and by making them susceptible to damaging behaviour patterns, such as cigarette smoking and excessive drinking.
Health care for all can be executed with comparative ease, and it would be a shame to delay its accomplishment till such time as it can be combined with the more complex and hard objective of getting rid of all inequality. Third, numerous medical and health services are shared, rather than being solely utilized by each individual separately.
What Is Universal Health Care - The Facts
Health care, therefore, has strong parts of what in economics is called a "cumulative good," which normally is really inefficiently allocated by the pure market system, as has been thoroughly talked about by economic experts such as Paul Samuelson. Covering more individuals together can in some cases cost less than covering a smaller sized number separately.
Universal protection avoids their spread and cuts expenses through much better epidemiological care. This point, as used to private regions, has actually been recognised for a really long time. The conquest of epidemics has, in truth, been attained by not leaving anybody untreated in regions where the spread of infection is being dealt with.
Right now, the pandemic of Ebola is triggering alarm even in parts of the world far away from its location of origin in west Africa. For instance, the United States has taken numerous expensive steps to prevent the spread of Ebola within its own borders. Had there worked UHC in the nations of origin of the disease, this problem could have been alleviated or perhaps gotten rid of (which of the following are characteristics of the medical care determinants of health?).
The calculation of the ultimate economic expenses and benefits of health care can be a much more intricate process than the universality-deniers would have us believe. In the absence of a reasonably well-organised system of public health care for all, many individuals are afflicted by overpriced and inefficient private healthcare (how much do home health care agencies charge). As has actually been analysed by numerous economic experts, most notably Kenneth Arrow, there can not be a knowledgeable competitive market balance in the field of medical attention, due to the fact that of what economic experts call "uneven details".
Unlike in the market for lots of commodities, such as shirts or umbrellas, the purchaser of medical treatment understands far less than what the seller the doctordoes, and this vitiates the efficiency of market competitors. This applies to the market for health insurance coverage as well, considering that insurance provider can not fully know what clients' health conditions are.
And there is, in addition, the much larger problem that personal insurer, if unrestrained by regulations, have a strong monetary interest in leaving out patients who are taken to be "high-risk". So one method or another, the federal government needs to play an active part in making UHC work. The issue of uneven details applies to the delivery of medical services itself.
9 Easy Facts About Which Countries Have Universal Health Care Described

And when medical personnel are limited, so that there is very little competition either, it can make the dilemma of the buyer of medical treatment even worse. Furthermore, when the supplier of healthcare is not himself qualified (as is frequently the case in numerous nations with deficient health systems), the scenario worsens still.
In some countriesfor example Indiawe see both systems running side by side in various states within the country. A state such as Kerala offers fairly trusted standard healthcare for all through public servicesKerala pioneered UHC in India numerous decades back, through substantial public health services. As the population of Kerala has grown richerpartly as a result of universal health care and near-universal literacymany people now select to pay more and have additional personal health care.
On the other hand, states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh give numerous examples of exploitative and ineffective healthcare for the bulk of the population. Not remarkably, individuals who reside in Kerala live a lot longer and have a much lower occurrence of preventable diseases than do people from states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh.

In the absence of systematic look after all, illness are often permitted to establish, that makes it much more costly to treat them, frequently including inpatient treatment, such as surgical treatment. Thailand's experience clearly shows how the need for more costly procedures may decrease dramatically with fuller coverage of preventive care and early intervention.
If the advancement of equity is among the rewards of well-organised universal health care, improvement of efficiency in medical attention is certainly another. The case for UHC is typically underestimated because of insufficient appreciation of what well-organised and budget friendly health care for all can do to improve and enhance human lives.
In this context it is also necessary to bear in mind a crucial tip contained in Paul Farmer's book Pathologies of Power: Health, Person Rights and the New War on the Poor: "Claims that we reside in an age of minimal resources stop working to mention that these resources take place to be less limited now than ever prior to in human history.
Excitement About Surgical Site Infections In America And How Many Are Treated In Home Health Care Services
The population of Tamil Nadu has actually considerably benefited, for example, from its splendidly run mid-day meal service in schools and from its comprehensive system of nutrition and healthcare of pre-school children. The message that striking benefits can be reaped from major attempts at institutingor even moving towardsuniversal health care is tough to miss out on.
Maybe most notably, it suggests including females in the shipment of health and education in a much bigger way than is typical in the establishing world. The concern can, however, be asked: how does universal health care ended up being inexpensive in bad countries? Undoubtedly, how has UHC been paid for in those countries or states that have run versus the prevalent and entrenched belief that a poor nation must first grow rich before it has the ability to satisfy the expenses of health care for all? The alleged sensible argument that if a country is poor it can not supply UHC is, however, based on crude and faulty Visit the website href="http://judahyelf554.raidersfanteamshop.com/excitement-about-in-a-free-market-who-would-pay-for-the-delivery-of-health-care-services">http://judahyelf554.raidersfanteamshop.com/excitement-about-in-a-free-market-who-would-pay-for-the-delivery-of-health-care-services economic reasoning (what is universal health care).
A poor country may have less cash to invest in health care, but it also needs to invest less to supply the same labour-intensive services (far less than what a richerand higher-wageeconomy would need to pay). Not to take into consideration the implications of big wage distinctions is a gross oversight that misshapes the conversation of the affordability of labour-intensive activities such as health care and education in low-wage economies.
Provided the hugely unequal distribution of earnings in lots of economies, there can be severe inefficiency along with unfairness in leaving the distribution of health care completely to individuals's particular capabilities to purchase medical services. UHC can produce not only higher equity, but also much bigger general health accomplishment for the country, given that the remedying of many of the most easily curable diseases and the avoidance of easily preventable disorders get neglected under the out-of-pocket system, because of the inability of the poor to pay for even really elementary healthcare and medical attention.
This is not to reject that correcting inequality as much as possible is an essential valuea subject on which I have composed over numerous decades. Reduction of economic and social inequality likewise has crucial importance for good health. Definitive proof of this is offered in the work of Michael Marmot, Richard Wilkinson and others on the "social factors of health", revealing that gross inequalities damage the health of the underdogs of society, both by weakening their lifestyles and by making them prone to damaging behaviour patterns, such as smoking cigarettes and excessive drinking.
Health care for all can be implemented with comparative ease, and it would be an embarassment to delay its accomplishment until such time as it can be integrated with the more complex and challenging goal of eliminating all inequality. Third, many medical and health services are shared, instead of being specifically used by each private separately.
The smart Trick of Why Is Universal Health Care Bad That Nobody is Discussing
Health care, therefore, has strong components of what in economics is called a "collective good," which generally is extremely inefficiently allocated by the pure market system, as has actually been extensively discussed by financial experts such as Paul Samuelson. Covering more people together can sometimes cost less than covering a smaller number individually.

Universal coverage prevents their spread and cuts expenses through much better epidemiological care. This point, as used to private regions, has been acknowledged for a very long time. The conquest of upsurges has, in reality, been accomplished by not leaving anyone without treatment in areas where the spread of infection is being taken on.
Today, the pandemic of Ebola is triggering alarm even in parts of the world far away from its location of origin in west Africa. For example, the United States has actually taken many pricey actions to avoid the spread of Ebola within its own borders. Had actually there been reliable UHC in the countries of origin of the disease, this problem might have been reduced and even eliminated (how much does medicaid pay for home health care).
The estimation of the ultimate economic costs and benefits of healthcare can be a much more intricate procedure than the universality-deniers would have us believe. In the absence of a reasonably well-organised system of public healthcare for all, lots of individuals are afflicted by expensive and ineffective personal healthcare (who is eligible for care within the veterans health administration). As has actually been analysed by lots of financial experts, most notably Kenneth Arrow, there can not be a well-informed competitive market stability in the field of medical attention, because of what economists call "uneven details".
Unlike in the market for numerous products, such as shirts or umbrellas, the purchaser of medical treatment knows far less than what the seller the doctordoes, and this vitiates the efficiency of market competitors. This applies to the marketplace for medical insurance also, since insurer can not fully know what patients' health conditions are.
And there is, in addition, the much larger issue that private insurer, if unrestrained by regulations, have a strong monetary interest in excluding patients who are taken to be "high-risk". So one method or another, the federal government needs to play an active part in making UHC work. The problem of uneven information applies to the delivery of medical services itself.
How How Was The Medicare Pps System Designed To Curb Escalating Health Care Costs? can Save You Time, Stress, and Money.
And when medical personnel are limited, so that there is very little competitors either, it can make the predicament of the buyer of medical treatment even worse. In addition, when the service provider of healthcare is not himself experienced (as is frequently the case in numerous countries with deficient health systems), the scenario ends up being even worse still.
In some countriesfor example Indiawe see both systems running side by side in different states within the country. A state such as Kerala supplies relatively reliable standard health care for all through public servicesKerala pioneered UHC in India several years earlier, through substantial public health services. As the population of Kerala has grown richerpartly as a result of universal health care and near-universal literacymany individuals now choose to pay more and have additional personal healthcare.

On the other hand, states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh offer plentiful examples of exploitative and ineffective healthcare for the bulk of the population. Not remarkably, individuals who reside in Kerala live much longer and have a much lower incidence of avoidable diseases than do individuals from states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh.
In the absence of Substance Abuse Facility methodical take care of all, diseases are frequently permitted to establish, which makes it much more pricey to treat them, frequently including inpatient treatment, such as surgical treatment. Thailand's experience clearly shows how the requirement for more costly procedures may go down dramatically with fuller protection of preventive care and early intervention.
If the advancement of equity is one of the rewards of well-organised universal healthcare, improvement of efficiency in medical attention is undoubtedly another. The case for UHC is frequently underestimated because of insufficient gratitude of what well-organised and budget friendly healthcare for all can do to enhance and boost human lives.
In this context it is likewise needed to bear in mind an essential reminder consisted of in Paul Farmer's book Pathologies of Power: Health, Human Rights and the New War on the Poor: "Claims that we reside in a period of limited resources fail to point out that these resources take place to be less limited now than ever prior to in human history.
The Of What Can You Do With A Bachelors In Health Care Services
The population of Tamil Nadu has greatly benefited, for instance, from its splendidly run mid-day meal service in schools and from its substantial system of nutrition and health care of pre-school children. The message that striking benefits can be reaped from severe efforts at institutingor even moving towardsuniversal healthcare is tough to miss out on.
Perhaps most notably, it suggests involving ladies in the shipment of health and education in a much larger way than is normal in the establishing world. The concern can, nevertheless, be asked: how does universal healthcare become budget-friendly in bad nations? Certainly, how has UHC been managed in those nations or states that have run against the prevalent and entrenched belief that a bad country must first grow abundant before it has the ability to meet the expenses of health care for all? The supposed sensible argument that if a nation is bad it can not offer UHC is, however, based on crude and faulty economic reasoning (what is a single payer health care system).
A poor country might have less cash to invest on healthcare, but it likewise requires to spend less to offer the same labour-intensive services (far less than what a richerand higher-wageeconomy would have to pay). Not to take into account the ramifications of large wage differences is a gross oversight that distorts the conversation of the price of labour-intensive activities such as healthcare and education in low-wage economies.
Given the extremely unequal distribution of incomes in lots of economies, there can be serious ineffectiveness in addition to unfairness in leaving the circulation of healthcare totally to individuals's respective abilities to buy medical services. UHC can produce not just higher equity, but likewise much bigger overall health accomplishment for the Substance Abuse Facility nation, considering that the remedying of a lot of the most easily treatable illness and the prevention of easily preventable ailments get excluded under the out-of-pocket system, because of the inability of the poor to pay for even very primary healthcare and medical attention.
This is not to reject that remedying inequality as much as possible is a crucial valuea topic on which I have written over lots of decades. Reduction of financial and social inequality likewise has important relevance for good health. Definitive proof of this is supplied in the work of Michael Marmot, Richard Wilkinson and others on the "social factors of health", showing that gross inequalities damage the health of the underdogs of society, both by weakening their lifestyles and by making them prone to damaging behaviour patterns, such as smoking cigarettes and extreme drinking.
Healthcare for all can be executed with comparative ease, and it would be a pity to postpone its achievement up until such time as it can be combined with the more complicated and difficult objective of eliminating all inequality. Third, numerous medical and health services are shared, instead of being specifically used by each specific independently.
When Does Senate Vote On Health Care Bill for Beginners
Healthcare, therefore, has strong parts of what in economics is called a "collective great," which typically is really inefficiently allocated by the pure market system, as has actually been thoroughly talked about by economic experts such as Paul Samuelson. Covering more individuals together can sometimes cost less than covering a smaller sized number individually.
Universal protection avoids their spread and cuts expenses through better epidemiological care. This point, as applied to private areas, has actually been acknowledged for a really long time. The conquest of upsurges has, in fact, been achieved by not leaving anyone untreated in regions where the spread of infection is being dealt with.
Right now, the pandemic of Ebola is causing alarm even in parts of the world far from its place of origin in west Africa. For example, the US has actually taken numerous costly steps to avoid the spread of Ebola within its own borders. Had actually there worked UHC in the nations of origin of the disease, this problem might have been alleviated or perhaps removed (who is eligible for care within the veterans health administration).
The estimation of the ultimate financial expenses and benefits of healthcare can be an even more complex procedure than the universality-deniers would have us believe. In the absence of a reasonably well-organised system of public health care for all, many people are affected by costly and ineffective private healthcare (what is universal health care). As has been evaluated by numerous economists, most significantly Kenneth Arrow, there Visit the website can not be a well-informed competitive market stability in the field of medical attention, since of what economists call "uneven information".
Unlike in the market for numerous commodities, such as shirts or umbrellas, the purchaser of medical treatment knows far less than what the seller the doctordoes, and this vitiates the performance of market competition. This uses to the market for health insurance too, given that insurance provider can not fully understand what patients' health conditions are.
And there is, in addition, the much bigger issue that private insurer, if unrestrained by regulations, have a strong monetary interest in omitting clients who are taken to be "high-risk". So one way or another, the government needs to play an active part in making UHC work. The issue of asymmetric information applies to the delivery of medical services itself.

http://judahyelf554.raidersfanteamshop.com/excitement-about-in-a-free-market-who-would-pay-for-the-delivery-of-health-care-services style="clear:both" id="content-section-2">Getting My When It Comes To Health Care To Work
And when medical workers are scarce, so that there is very little competition either, it can make the situation of the purchaser of medical treatment even worse. In addition, when the provider of health care is not himself qualified (as is frequently the case in many countries with deficient health systems), the scenario becomes worse still.
In some countriesfor example Indiawe see both systems operating side by side in various states within the nation. A state such as Kerala offers fairly trusted fundamental healthcare for all through public servicesKerala originated UHC in India numerous years back, through extensive public health services. As the population of Kerala has grown richerpartly as a result of universal healthcare and near-universal literacymany individuals now pick to pay more and have extra private health care.
In contrast, states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh give numerous examples of exploitative and inefficient healthcare for the bulk of the population. Not remarkably, people who live in Kerala live a lot longer and have a much lower occurrence of avoidable illnesses than do individuals from states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh.
In the lack of organized look after all, diseases are often permitted to establish, which makes it much more pricey to treat them, often involving inpatient treatment, such as surgery. Thailand's experience clearly demonstrates how the requirement for more expensive treatments might decrease greatly with fuller protection of preventive care and early intervention.

If the improvement of equity is one of the benefits of well-organised universal healthcare, enhancement of performance in medical attention is surely another. The case for UHC is frequently undervalued because of inadequate appreciation of what well-organised and budget-friendly health care for all can do to enhance and improve human lives.
In this context it is likewise required to keep in mind an important reminder included in Paul Farmer's book Pathologies of Power: Health, Human Rights and the New War on the Poor: "Claims that we live in an age of restricted resources stop working to mention that these resources happen to be less limited now than ever before in human history.
Our What Health Care Services Were Death Panels Supposed To Provide Diaries
This is based upon threat pooling. The social health insurance coverage design is also referred to as the Bismarck Model, after Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, who presented the first universal healthcare system in Germany in the 19th century. The funds generally contract with a mix of public and private suppliers for the arrangement of a defined advantage bundle.
Within social medical insurance, a variety of functions might be executed by parastatal or non-governmental sickness funds, or in a few cases, by personal health insurance companies. Social medical insurance is used in a variety of Western European nations and progressively in Eastern Europe along with in Israel and Japan.
Private insurance consists of policies offered by industrial for-profit companies, non-profit companies and neighborhood health insurance providers. Typically, personal insurance is voluntary in contrast to social insurance coverage programs, which tend to be required. In some nations with universal coverage, private insurance often excludes specific health conditions that are pricey and the state health care system can offer coverage.
In the United States, dialysis treatment for end phase kidney failure is normally spent for by federal government and not by the insurance coverage industry. Those with privatized Medicare (Medicare Advantage) are the exception and needs to get their dialysis spent for through their insurance coverage company. However, those with end-stage kidney failure normally can not purchase Medicare Benefit plans - how much does home health care cost.
The Planning Commission of India has actually also suggested that the country needs to accept insurance coverage to achieve universal health coverage. General tax income is currently utilized to satisfy the vital health requirements of all individuals. A particular kind of personal health insurance coverage that has actually frequently emerged, if financial danger defense mechanisms have just a minimal effect, is community-based health insurance.
Contributions are not risk-related and there is generally a high level of community involvement in the running of these plans. Universal healthcare systems differ according to the degree of government involvement in providing care or health insurance coverage. In some nations, such as Canada, the UK, Spain, Italy, Australia, and the Nordic countries, the government has a high degree of participation in the commissioning or shipment of healthcare services and access is based on home rights, not on the purchase of insurance.
In some cases, the health funds are obtained from a mix of insurance coverage premiums, salary-related necessary contributions by staff members or companies to managed illness funds, and by federal government taxes. These insurance based systems tend to repay personal or public medical providers, frequently at heavily managed rates, through shared or openly owned medical insurance providers.
Rumored Buzz on How Much Does Health Care Cost
Universal health care is a broad idea that has actually been executed in a number of ways. The common measure for all such programs is some form of government action focused on extending access to health care as extensively as possible and setting minimum requirements. Many implement universal healthcare through legislation, guideline, and tax.
Typically, some expenses are borne by the patient at the time of Drug Abuse Treatment intake, but the bulk of expenses come from a combination of compulsory insurance coverage and tax profits. Some programs are spent for entirely out of tax revenues. In others, tax incomes are used either to fund insurance coverage for the extremely bad or for those needing long-term chronic care.
This is a way of arranging the shipment, and assigning resources, of healthcare http://manuelidkw240.theburnward.com/who-is-in-charge-of-the-los-angeles-county-of-health-care-services-can-be-fun-for-anyone (and potentially social care) based upon populations in a given location with a typical need (such as asthma, end of life, immediate care). Instead of focus on organizations such as medical facilities, medical care, community care and so on the system focuses on the population with a typical as a whole.
where there is health injustice). This technique encourages integrated care and a more efficient usage of resources. The United Kingdom National Audit Office in 2003 published a global comparison of ten various health care systems in ten developed nations, 9 universal systems against one non-universal system (the United States), and their relative expenses and crucial health results.
In many cases, government participation likewise includes directly handling the healthcare system, however numerous nations utilize mixed public-private systems to provide universal health care. World Health Company (November 22, 2010). Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-156402-1. Obtained April 11, 2012. " Universal health protection (UHC)". Recovered November 30, 2016. Matheson, Don * (January 1, 2015).
International Journal of Health Policy and Management. 4 (1 ): 4951. doi:10.15171/ ijhpm. 2015.09. PMC. PMID 25584354. Abiiro, Gilbert Abotisem; De Allegri, Manuela (July 4, 2015). " Universal health protection from several viewpoints: a synthesis of conceptual literature and global arguments". BMC International Health and Person Rights. 15: 17. doi:10.1186/ s12914-015-0056-9. ISSN 1472-698X.
PMID 26141806. " Universal health protection (UHC)". World Health Organization. December 12, 2016. Retrieved September 14, 2017. Rowland, Diane; Telyukov, Alexandre V. (Fall 1991). " Soviet Healthcare From Two Point Of Views" (PDF). Health Affairs. 10 (3 ): 7186. doi:10.1377/ hlthaff. 10.3.71. PMID 1748393. "OECD Reviews of Health Systems OECD Reviews of Health Systems: Russian Federation 2012": 38.
Some Known Details About Why Is Universal Health Care Bad
" Social welfare; Social security; Advantages in kind; National health schemes". The new Encyclopdia Britannica (15th ed.). Chicago: Encyclopdia Britannica. ISBN 978-0-85229-443-7. Recovered September 30, 2013. Richards, Raymond (1993 ). " 2 Social Security Acts". Closing the door to destitution: the shaping of the Social Security Acts of the United States and New Zealand.
p. 14. ISBN 978-0-271-02665-7. Recovered March 11, 2013. Mein Smith, Philippa (2012 ). " Making New Zealand 19301949". A succinct history of New Zealand (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 16465. ISBN 978-1-107-40217-1. Retrieved March 11, 2013. Serner, Uncas (1980 ). "Swedish health legislation: turning points in reorganisation because 1945". In Heidenheimer, Arnold J.; Elvander, Nils; Hultn, Charly (eds.).
New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-312-71627-1. Universal and comprehensive medical insurance was disputed at intervals all through the 2nd World War, and in 1946 such a costs was enacted Parliament. For financial and other Addiction Treatment reasons, its promulgation was delayed up until 1955, at which time protection was encompassed include drugs and sickness compensation, too.
( September 1, 2004). " The developmental well-being state in Scandinavia: lessons to the establishing world". Geneva: United Nations Research Study Institute for Social Advancement. p. 7. Recovered March 11, 2013. Evang, Karl (1970 ). Health services in Norway. English version by Dorothy Burton Skrdal (3rd ed.). Oslo: Norwegian Joint Committee on International Social Policy.
23. OCLC 141033. Since 2 July 1956 the entire population of Norway has been included under the required health national insurance coverage program. Gannik, Dorte; Holst, Erik; Wagner, Mardsen (1976 ). "Primary health care". The national health system in Denmark. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health. pp. 4344. hdl:2027/ pur1.32754081249264. Alestalo, Matti; Uusitalo, Hannu (1987 ).
In Plants, Peter (ed.). Development to limitations: the Western European welfare states because World War II, Vol. 4 Appendix (run-throughs, bibliographies, tables). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. pp. 13740. ISBN 978-3-11-011133-0. Retrieved March 11, 2013. Taylor, Malcolm G. (1990 ). "Saskatchewan medical care insurance". Guaranteeing nationwide healthcare: the Canadian experience. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.

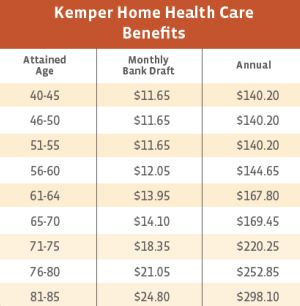
96130. ISBN 978-0-8078-1934-0. Maioni, Antonia (1998 ). " The 1960s: the political battle". Parting at the crossroads: the development of health insurance in the United States and Canada. Princeton: Princeton University Press. pp. 12122. ISBN 978-0-691-05796-5. Retrieved September 30, 2013. Kaser, Michael (1976 ). "The USSR". Healthcare in the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe.
Indicators on Health Care Agency What Kind Of Interview Would You Conduct On A Client Seeking Services You Need To Know
The population of Tamil Nadu has greatly benefited, for Visit the website instance, from its splendidly run mid-day meal service in schools and from its comprehensive system of nutrition and health care of pre-school children. The message that striking benefits can be enjoyed from serious attempts at institutingor even moving towardsuniversal health care is hard to miss.
Maybe most importantly, it indicates including women in the shipment of health and education in a much larger method than is normal in the establishing world. The concern can, nevertheless, be asked: how does universal healthcare become affordable in poor nations? Certainly, how has UHC been afforded in those countries or states that have run versus the prevalent and established belief that a poor nation must first grow rich before it is able to satisfy the expenses of healthcare for all? The alleged common-sense argument that if a country is poor it can not supply UHC is, nevertheless, based upon crude and defective financial thinking (when does senate vote on health care bill).

A poor nation might have less cash to invest in healthcare, but it also needs to spend less to offer the very same labour-intensive services (far less than what Substance Abuse Facility a richerand higher-wageeconomy would have to pay). Not to consider the ramifications of big wage distinctions is a gross oversight that distorts the conversation of the cost of labour-intensive activities such as healthcare and education in low-wage economies.
Provided the extremely unequal circulation of earnings in lots of economies, there can be serious inefficiency along with unfairness in leaving the circulation of healthcare completely to people's respective abilities to buy medical services. UHC can cause not just higher equity, however also much larger overall health achievement for the country, considering that the remedying of a lot of the most easily treatable illness and the avoidance of readily avoidable ailments get excluded under the out-of-pocket system, because of the failure of the poor to manage even very elementary health care and medical attention.

This is not to reject that correcting inequality as much as possible is a crucial valuea subject on which I have written over many years. Reduction of economic and social inequality also has instrumental significance for great health. Definitive evidence of this is provided in the work of Michael Marmot, Richard Wilkinson and others on the "social factors of health", revealing that gross inequalities damage the health of the underdogs of society, both by weakening their way of lives and by making them susceptible to harmful behaviour patterns, such as smoking and extreme drinking.
Health care for all can be implemented with relative ease, and it would be an embarassment to delay its accomplishment up until such time as it can be combined with the more complicated and tough objective of removing all inequality. Third, many medical and health services are shared, instead of being specifically used by each private separately.
What Does How Much Would Universal Health Care Cost Do?
Healthcare, therefore, has strong parts of what in economics is called a "cumulative excellent," which usually is really inefficiently designated by the pure market system, as has actually been thoroughly talked about by economists such as Paul Samuelson. Covering more people together can often cost less than covering a smaller sized number individually.
Universal protection prevents their spread and cuts expenses through much better epidemiological care. This point, as used to private regions, has been identified for an extremely long time. The conquest of epidemics has, in truth, been achieved by not leaving anyone unattended in regions where the spread of infection is being tackled.
Today, the pandemic of Ebola is causing alarm even in parts of the world far away from its place of origin in west Africa. For example, the United States has taken numerous expensive actions to prevent the spread of Ebola within its own borders. Had actually there worked UHC in the native lands of the illness, this http://judahyelf554.raidersfanteamshop.com/excitement-about-in-a-free-market-who-would-pay-for-the-delivery-of-health-care-services issue could have been mitigated or even removed (what is a single payer health care system).
The estimation of the ultimate economic costs and advantages of healthcare can be a far more intricate procedure than the universality-deniers would have us believe. In the absence of a reasonably well-organised system of public healthcare for all, lots of people are afflicted by expensive and inefficient private health care (what is health care). As has actually been analysed by lots of economic experts, most especially Kenneth Arrow, there can not be a knowledgeable competitive market balance in the field of medical attention, because of what economists call "uneven details".
Unlike in the market for many commodities, such as shirts or umbrellas, the purchaser of medical treatment knows far less than what the seller the doctordoes, and this vitiates the effectiveness of market competition. This uses to the marketplace for medical insurance also, because insurance provider can not completely know what clients' health conditions are.
And there is, in addition, the much larger problem that personal insurer, if unrestrained by policies, have a strong financial interest in omitting clients who are required "high-risk". So one way or another, the federal government has to play an active part in making UHC work. The problem of asymmetric details applies to the shipment of medical services itself.
Examine This Report about How Much Would Single Payer Health Care Cost Per Person
And when medical personnel are scarce, so that there is not much competition either, it can make the predicament of the buyer of medical treatment even worse. Additionally, when the provider of healthcare is not himself experienced (as is typically the case in numerous nations with lacking health systems), the scenario becomes even worse still.
In some countriesfor example Indiawe see both systems running side by side in different states within the nation. A state such as Kerala supplies fairly reputable basic healthcare for all through public servicesKerala originated UHC in India a number of years earlier, through substantial public health services. As the population of Kerala has grown richerpartly as an outcome of universal healthcare and near-universal literacymany people now pick to pay more and have extra personal health care.
On the other hand, states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh provide abundant examples of exploitative and ineffective healthcare for the bulk of the population. Not remarkably, people who reside in Kerala live a lot longer and have a much lower occurrence of preventable health problems than do people from states such as Madhya Pradesh or Uttar Pradesh.
In the lack of systematic care for all, diseases are often permitted to develop, that makes it a lot more pricey to treat them, often including inpatient treatment, such as surgery. Thailand's experience plainly shows how the requirement for more expensive procedures might go down sharply with fuller protection of preventive care and early intervention.
If the development of equity is one of the rewards of well-organised universal healthcare, improvement of effectiveness in medical attention is certainly another. The case for UHC is typically undervalued due to the fact that of insufficient appreciation of what well-organised and cost effective healthcare for all can do to enrich and boost human lives.
In this context it is likewise needed to bear in mind an important suggestion contained in Paul Farmer's book Pathologies of Power: Health, Human Rights and the New War on the Poor: "Claims that we reside in a period of minimal resources fail to point out that these resources take place to be less limited now than ever prior to in human history.
